All Related Articles



Illustrating Senator Warren’s Taxes on Capital Income
Taken together, these proposed tax changes would significantly raise marginal and effective tax rates and increase the cost of capital, all of which would lead to a reduced level of output and less revenue than anticipated.
5 min read
2020 Tax Brackets
The IRS recently released the new 2020 tax brackets and rates. Explore updated credits, deductions, and exemptions, including the standard deduction & personal exemption, Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT), Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), Child Tax Credit (CTC), capital gains brackets, qualified business income deduction (199A), and the annual exclusion for gifts.
5 min read
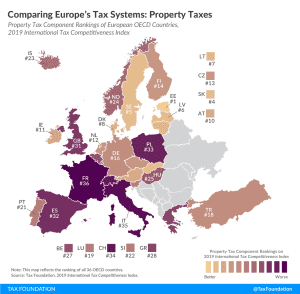
Welcome to the Index, Lithuania!
5 min read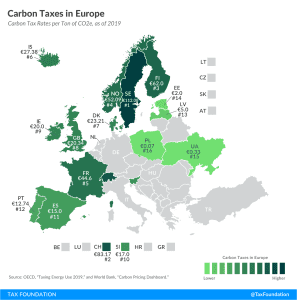
Carbon Taxes in Europe, 2019
3 min read

Proponents of Wealth Taxation Must Consider its Impact on Innovation
Instead of raising revenue from a narrow tax base through high tax rates, policymakers should identify options to raise revenue efficiently through broad-based taxes consistent with sound tax policy.
4 min read
Wireless Taxes and Fees Jump Sharply In 2019
Wireless taxes, fees, and surcharges make up over 20% of the average customer’s bill–the highest rate ever. Illinois has the highest wireless taxes in the country at over 30%, followed by Washington, Nebraska, New York, and Utah. How high are cell phone taxes in your state?
36 min read

Reviewing the Deadweight Loss Effects of High Tax Rates
Deadweight loss effects demonstrate why policymakers should pursue a more efficient tax code to achieve distributional objectives, rather than pursuing high tax rates that create disproportionately high economic costs.
4 min read


Carbon Tax and Revenue Recycling: Revenue, Economic, and Distributional Implications
In our new report, we explore the design implications of a carbon tax and provide estimates for revenue, economic, and distributional effects of three potential carbon tax and revenue recycling proposals. Each proposal faces different trade-offs and achieves different policy goals.
23 min read
Results of 2019 State and Local Tax Ballot Initiatives
Election Day 2019 will feature notable tax-related ballot measures in California, Colorado, New Mexico, Pennsylvania, Texas, and Washington. Once the polls close tonight, beginning with Pennsylvania and Texas at 8 PM EST, we will begin tracking the results as they come in.
4 min read