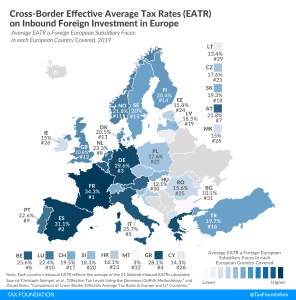
New Jersey Waives Telework Nexus During COVID-19 Crisis
New Jersey is temporarily waiving corporate nexus arising from employees teleworking due to the COVID-19 pandemic—a response to the crisis that other states should follow.
3 min read
New Jersey is temporarily waiving corporate nexus arising from employees teleworking due to the COVID-19 pandemic—a response to the crisis that other states should follow.
3 min read
The CARES Act, now signed into law, is intended to be a third round of federal government support in the wake of the coronavirus public health crisis and associated economic fallout, following the $8.3 billion in public health support passed two weeks ago and the Families First Coronavirus Response Act.
10 min read
Spain’s policy response needs to be broad and in keeping with long-term objectives. It is paramount that the short-term harm caused by this outbreak does not turn into a long-term economic downturn.
5 min read
Policymakers must weigh the trade-offs of subsidizing unemployment with mitigating community spread of coronavirus.
6 min read
Even during the coronavirus outbreak, efforts to change the way digital business models are taxed continue. India announced this week that its tax aimed at foreign digital companies, the “equalization levy,” will be expanded.
4 min read
Denmark, a high-tax country with 5.5 million citizens, has implemented policies designed to avoid layoffs and bankruptcies and basically unplug the economy during the pandemic.
4 min read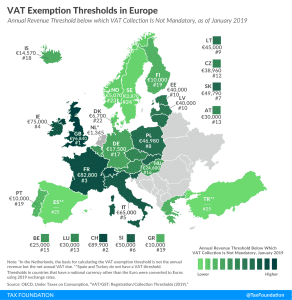
Due to certain VAT exemption thresholds, many small businesses will not be able to benefit from the VAT changes being introduced throughout Europe to provide relief during the COVID-19 crisis.
2 min read
One of the most talked about government economic responses to the COVID-19 crisis is Germany’s Kurzarbeit: the German short-work subsidy scheme.
3 min read
To be eligible for federal funding, state expenditures must meet certain conditions. We break down the state aid coronavirus provisions in the latest federal bill.
5 min read
During the present crisis, remote work has become a necessity for many people. The tax implications, however, are very real and potentially quite complex.
7 min read
Countries around the world are implementing emergency tax measures to support their economies under the coronavirus (COVID-19) threat.
51 min read
Norway passed a large coronavirus tax relief package to address layoffs and bankruptcies, which includes a reduced VAT rate, the introduction of a loss carryback provision, and targeted postponements for wealth tax payments, among other provisions.
5 min read
The proposed Take Responsibility for Workers and Families Act can be contrasted with the Senate Republican CARES Act, although they share some similarities by providing individual taxpayers with a rebate and modifying business tax provisions to provide liquidity for struggling firms.
5 min read
As lawmakers debate how to respond to the coronavirus crisis, they should focus the legislative response to the emergency at hand, using principled policy solutions to provide relief to those affected. Attempts to use the crisis to make other, unrelated policy changes should be avoided.
3 min read
Countries around the world are implementing emergency tax measures to support their debilitated economies under the coronavirus (COVID-19) threat.
7 min read
Unemployment claims are going to tax state unemployment compensation trust funds beyond their limits. We need to start thinking about what to do about it.
5 min read
The federal government moved tax day from April 15 to July 15 in response to the coronavirus pandemic, granting more time for both filing and payment. But for many taxpayers, it might not matter much if states don’t follow suit.
3 min read
The U.S. Treasury Department has pushed the April 15 tax payment deadline to July 15. However, taxpayers still have to file their tax returns by the usual April 15 deadline.
3 min read
During the coronavirus outbreak, Italy has been hit especially hard. Policymakers have introduced numerous measures to stem the spread of the virus and provide relief to businesses that are facing a severe downturn.
2 min read