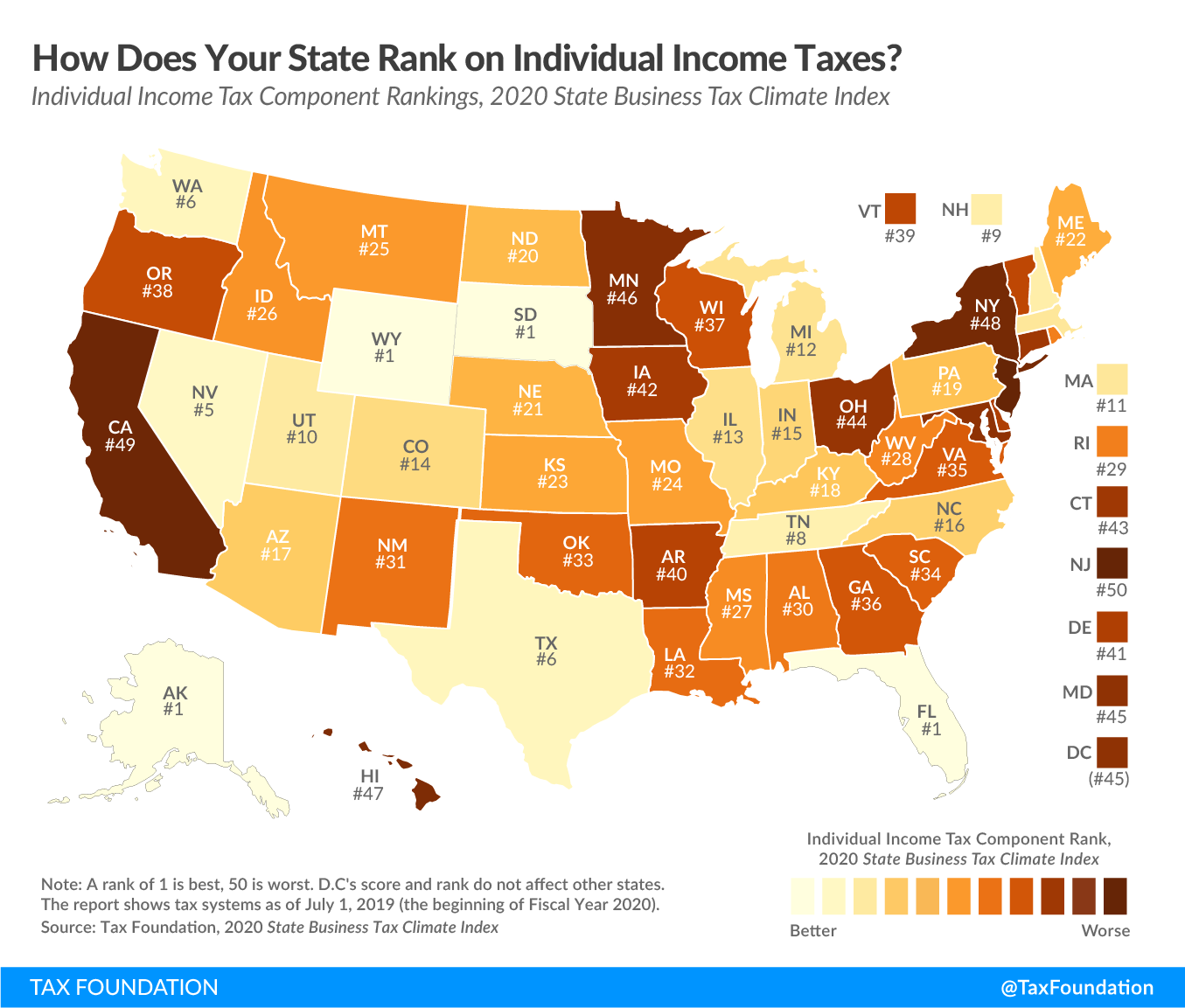
This week’s map examines states’ rankings on the individual income taxAn individual income tax (or personal income tax) is levied on the wages, salaries, investments, or other forms of income an individual or household earns. The U.S. imposes a progressive income tax where rates increase with income. The Federal Income Tax was established in 1913 with the ratification of the 16th Amendment. Though barely 100 years old, individual income taxes are the largest source of tax revenue in the U.S. component of the 2020 State Business Tax Climate Index. The individual income tax is important to businesses because states taxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities. sole proprietorships, partnerships, and in most cases, limited liability companies (LLCs) and S corporations, under the individual income tax code. However, even traditional C corporations are indirectly impacted by the individual income tax, as this tax influences the location decisions of individuals, potentially impacting the state’s labor supply. States with gross receipts taxes also extend those to pass-through businesses in addition to C corporations, which are also accounted for in this component of the Index.
States that score well on the Index’s individual income tax component usually have a flat, low-rate income tax with few deductions and exemptions. They also tend to protect married taxpayers from being taxed more heavily when filing jointly than they would be when filing as two single individuals. In addition, states perform better on the Index’s individual income tax component if they index their brackets, deductions, and exemptions for inflation, which avoids unlegislated tax increases.
States with a perfect score on the individual income tax component (Alaska, Florida, South Dakota, and Wyoming) have no individual income tax and no payroll taxes besides the unemployment insurance tax. The next highest-scoring states are Nevada, Texas, Washington, Tennessee, and New Hampshire. Nevada taxes wage income at a low rate under the state’s Modified Business Tax but does not tax investment income. Tennessee and New Hampshire tax interest and dividend income but not wage income. Texas and Washington do not tax wage income but don’t receive a perfect score on this component because they apply their gross receipts taxes to LLCs and S corporations, which, in most states, would be taxed under individual income tax codes. Other states that score well on the individual income tax component are Colorado, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Massachusetts, Michigan, North Carolina, and Utah, because they all have a single low tax rate.
States that score poorly on this component tend to have high tax rates and very progressive bracket structures. They generally fail to index their brackets, exemptions, and deductions for inflationInflation is when the general price of goods and services increases across the economy, reducing the purchasing power of a currency and the value of certain assets. The same paycheck covers less goods, services, and bills. It is sometimes referred to as a “hidden tax,” as it leaves taxpayers less well-off due to higher costs and “bracket creep,” while increasing the government’s spending power. , do not allow the deduction of foreign or other state taxes, penalize married couples filing jointly, do not include LLCs and S corporations under the individual income tax code, and may impose an alternative minimum tax (AMT). The poorest-performing states on this year’s individual income tax component are New Jersey, California, New York, Hawaii, and Minnesota.
Click here to see an interactive version of states’ individual income tax rankings, and then click on your state for more information about how its tax system compares regionally and nationally.
To see whether your state’s individual income tax structure has moved up or down in the ranks in recent years, check out the table below.
|
Note: A rank of 1 is best, 50 is worst. All scores are for fiscal years. DC’s score and rank do not affect other states. Source: Tax Foundation. |
|||||
| State | 2017 Rank | 2018 Rank | 2019 Rank | 2020 Rank | Change from 2019 to 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 28 | 28 | 30 | 30 | 0 |
| Alaska | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Arizona | 18 | 18 | 19 | 17 | 2 |
| Arkansas | 39 | 39 | 40 | 40 | 0 |
| California | 50 | 50 | 49 | 49 | 0 |
| Colorado | 16 | 16 | 14 | 14 | 0 |
| Connecticut | 46 | 46 | 43 | 43 | 0 |
| Delaware | 43 | 43 | 41 | 41 | 0 |
| Florida | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Georgia | 36 | 36 | 38 | 36 | 2 |
| Hawaii | 37 | 37 | 47 | 47 | 0 |
| Idaho | 21 | 21 | 24 | 26 | -2 |
| Illinois | 12 | 15 | 13 | 13 | 0 |
| Indiana | 10 | 10 | 15 | 15 | 0 |
| Iowa | 40 | 40 | 42 | 42 | 0 |
| Kansas | 19 | 19 | 22 | 23 | -1 |
| Kentucky | 35 | 35 | 17 | 18 | -1 |
| Louisiana | 33 | 33 | 32 | 32 | 0 |
| Maine | 24 | 26 | 25 | 22 | 3 |
| Maryland | 45 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 0 |
| Massachusetts | 13 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 0 |
| Michigan | 14 | 14 | 12 | 12 | 0 |
| Minnesota | 44 | 44 | 46 | 46 | 0 |
| Mississippi | 25 | 24 | 27 | 27 | 0 |
| Missouri | 32 | 31 | 26 | 24 | 2 |
| Montana | 20 | 20 | 23 | 25 | -2 |
| Nebraska | 22 | 22 | 21 | 21 | 0 |
| Nevada | 1 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| New Hampshire | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 0 |
| New Jersey | 48 | 48 | 50 | 50 | 0 |
| New Mexico | 27 | 27 | 31 | 31 | 0 |
| New York | 49 | 49 | 48 | 48 | 0 |
| North Carolina | 15 | 13 | 16 | 16 | 0 |
| North Dakota | 23 | 23 | 20 | 20 | 0 |
| Ohio | 47 | 47 | 44 | 44 | 0 |
| Oklahoma | 30 | 32 | 33 | 33 | 0 |
| Oregon | 38 | 38 | 36 | 38 | -2 |
| Pennsylvania | 17 | 17 | 18 | 19 | -1 |
| Rhode Island | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 0 |
| South Carolina | 31 | 30 | 34 | 34 | 0 |
| South Dakota | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Tennessee | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 0 |
| Texas | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 |
| Utah | 11 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 0 |
| Vermont | 42 | 42 | 37 | 39 | -2 |
| Virginia | 34 | 34 | 35 | 35 | 0 |
| Washington | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 |
| West Virginia | 26 | 25 | 28 | 28 | 0 |
| Wisconsin | 41 | 41 | 39 | 37 | 2 |
| Wyoming | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| District of Columbia | 48 | 48 | 45 | 45 | 0 |
Note: This map is part of a series in which we will examine each of the five major components of our 2020 State Business Tax Climate Index.
Stay informed on the tax policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted experts delivered straight to your inbox.
Subscribe