Krispy Kreme may have started the vaccine incentive ball rolling, but many states are putting big money into the effort with vaccine lotteries. Unlike a normal lottery, no one is paying for tickets—but the tax collector still gets paid when someone wins.
With lots of restricted spending COVID-19 relief funds and a substantial number of unvaccinated residents, Ohio decided the time was ripe for a vaccine lottery, giving out five $1 million prizes among those 18 and over who get the shot. Maryland, New York, Washington, and West Virginia quickly followed in Ohio’s footsteps, setting up their own vaccine lotteries.
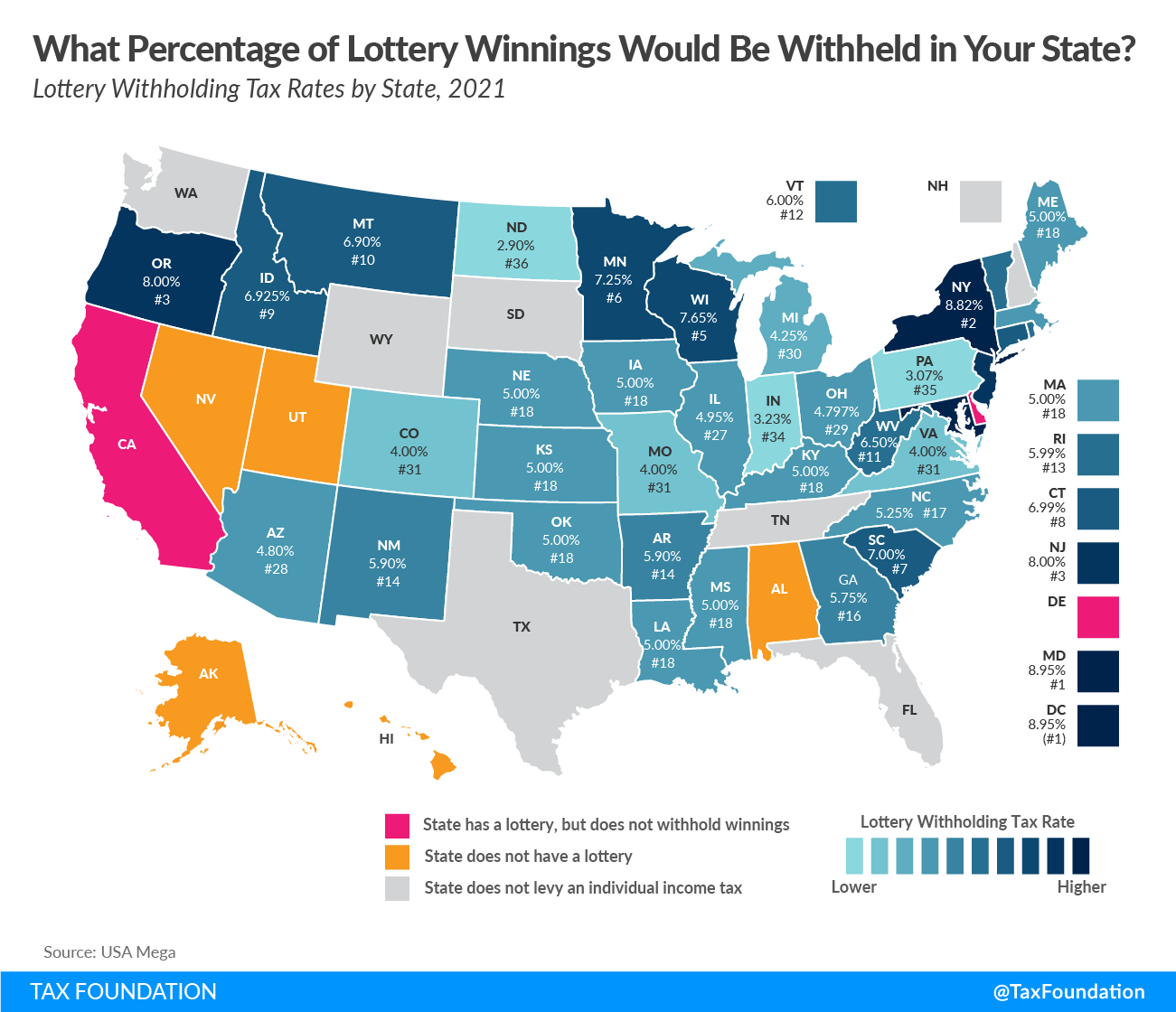
Residents’ odds of winning a cash prize are long, but the government cut of the winnings is guaranteed. That’s because lottery winnings—all lottery winnings, including these unique vaccine lotteries—are generally taxed as ordinary income at the federal and state levels (and, where applicable, locally). In fact, most states (and the federal government) automatically withhold taxes on lottery winnings over $5,000. However, withholding rates vary and do not always match state individual income taxes.
- California does not taxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities. state lottery winnings.
- Delaware taxes winnings at its normal state rates but does not withhold.
- Arizona and Maryland have separate resident and nonresident withholdingWithholding is the income an employer takes out of an employee’s paycheck and remits to the federal, state, and/or local government. It is calculated based on the amount of income earned, the taxpayer’s filing status, the number of allowances claimed, and any additional amount of the employee requests. rates.
- In New York, residents of New York City and Yonkers face additional withholdings of 3.876 percent and 1.477 percent, respectively.
And of course, withholding rates sometimes differ from the top marginal rate, because states account for lottery winners’ effective rates on winnings being lower than the top marginal rate, given various exemptions, credits, and deductions, and the nature of graduated taxes.
As you might expect, winners in states which forgo individual income taxes or exempt lottery winnings fare the best. States which do not withhold winnings offer some advantages too, but the tax bill still has to be paid. At the other end of the spectrum, states with high withholding rates effectively receive a no-interest loan from winners who overpay, until tax returns are filed and a refund is processed.
In the case of Ohio and other states with a vaccine lottery, governments have the additional benefit of getting back a portion of their relief funds—but without spending restrictions this time.
Vaccine lottery prizes differ too much to compare among states, but the Mega Millions jackpot (back to $20 million after a $56 million winner on Tuesday) can give us a sense of state differences. Lump sum after-tax payouts at the level of a $56 million jackpot winner will vary considerably across the country, ranging from the lowest in New York at $20,480,468 to a high of $24,164,928 in states either forgoing an individual income taxAn individual income tax (or personal income tax) is levied on the wages, salaries, investments, or other forms of income an individual or household earns. The U.S. imposes a progressive income tax where rates increase with income. The Federal Income Tax was established in 1913 with the ratification of the 16th Amendment. Though barely 100 years old, individual income taxes are the largest source of tax revenue in the U.S. or exempting state lottery winnings. This includes federal withholding of 24 percent ($9.19 million), though federal liability could ultimately be much higher, particularly if the winner isn’t feeling very charitable with his or her prize.
Share this article