More voices are entering the fray to call out the problem of growing U.S. deficits, which are on track to reach nearly 7 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) by the decade’s end. Rather than continue down the path of growing debt, lawmakers should craft a comprehensive solution. International experience cautions against taxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities. -based fiscal consolidations, but modest tax increases may be part of a successful debt reduction package. In this blog post, we explore how to design tax increases to stabilize the debt. The next blog post in our debt and deficits series considers how to design spending cuts.
Design is important because raising a dollar of revenue through different taxes has different effects on the economy. A more harmful tax increase can shrink the economy, yielding less revenue from other taxes. Harm the economy too much and the solution may prove counter-productive, reducing the likelihood of successful debt stabilization.
These points bear out in the economic literature. Tax-based deficit reductions tend to have a more negative impact on the economy and less successful track record than spending-based ones. The difference is primarily due to the response of private investment, as business confidence falls to a greater degree and for a much longer duration after tax-based plans.
Overall, successful fiscal adjustments primarily cut spending and modestly increase taxes. A rough guideline for an expenditure-based plan is for at least 60 percent of its savings to come from spending cuts and 40 percent or less from revenues. Applied to the U.S. context, stabilizing debt at its current share of GDP would require about $8 trillion in 10-year savings, with a $3 trillion limit on tax increases.
Research from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) emphasizes avoiding economically damaging taxes in fiscal consolidation packages. Raising corporate or personal income taxes is a no-go. Instead, less harmful tax types, like consumption or environmental taxes, and base broadening efforts should be in the mix.
Tax Foundation similarly concludes that not all taxes are created equal. We can categorize taxes in a hierarchy of most to least harmful, largely based on how responsive an activity is to taxation. Corporate income taxes are the most harmful because capital is highly mobile. Individual income taxes come next, followed by relatively less harmful payroll and consumption taxes.
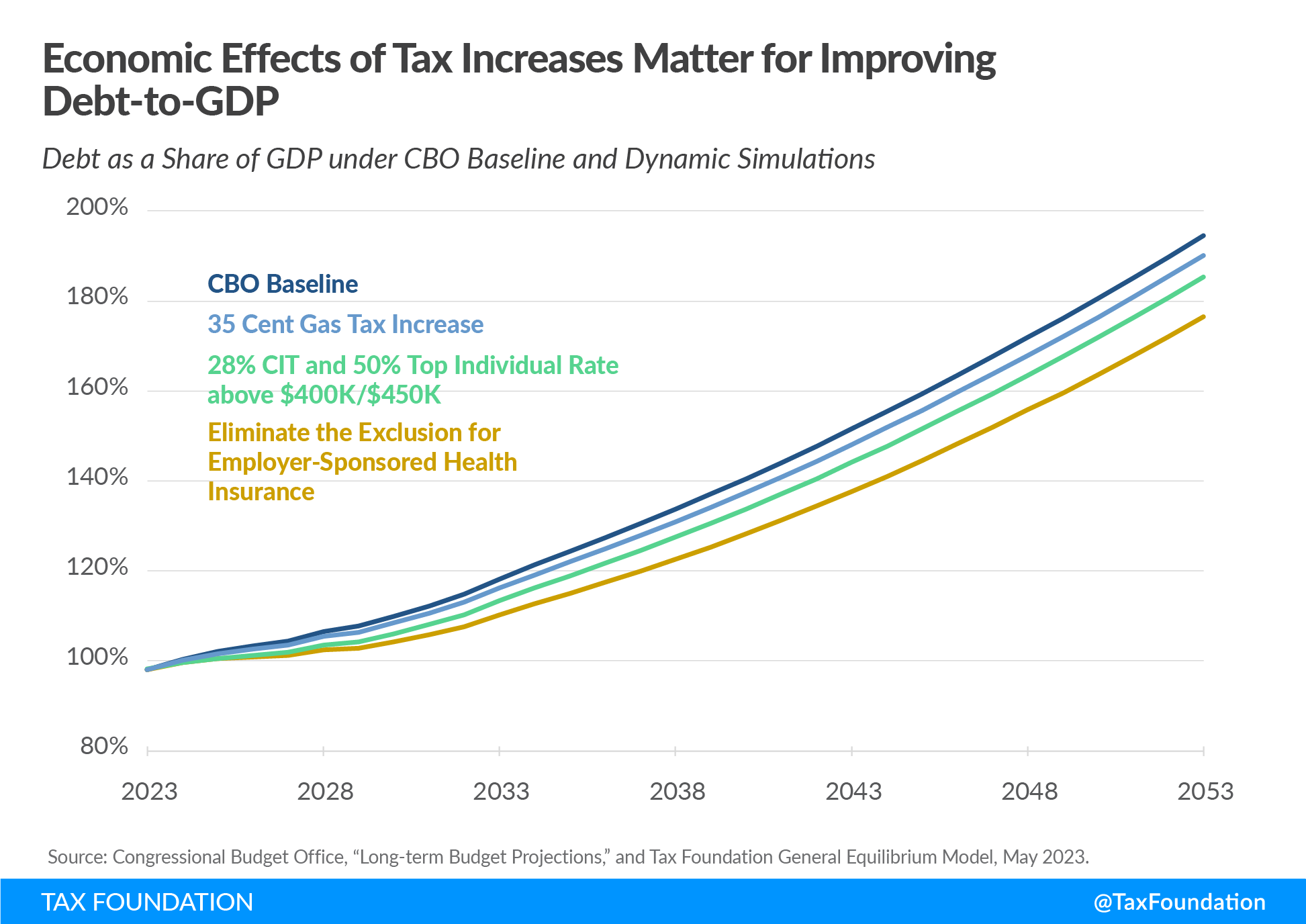
The table and chart below illustrate how modest tax increases with minimal harm to the economy can contribute to debt stabilization.
Compare increasing the gas tax by $0.35 and inflation-indexing it, broadening the individual income tax base by eliminating the exclusion for employer-sponsored health insurance (ESI), or raising the top individual income tax rate to 50 percent above $400,000 for single filers and $450,000 for joint filers and the corporate tax rate to 28 percent.
| Raise the Gas Tax by $0.35 | Eliminate the Exclusion for Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance | 28% CIT and 50% Top Individual Rate above $400K/$450K | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long-Run GDP | -0.2% | -0.5% | -1.3% |
| Conventional Revenue, 2024-2033 (Billions) | $931 | $3,523 | $2,872 |
| Dynamic Revenue, 2024-2033 (Billions) | $797 | $3,117 | $2,151 |
| Dynamic Improvement in Debt-to-GDP Ratio, 2033 | 2 percentage points | 8 percentage points | 5 percentage points |
| Dynamic Improvement in Debt-to-GDP Ratio, Long Run | 4 percentage points | 18 percentage points | 9 percentage points |
|
Source: Tax Foundation General Equilibrium Model, May 2023. |
|||
The base broadeningBase broadening is the expansion of the amount of economic activity subject to tax, usually by eliminating exemptions, exclusions, deductions, credits, and other preferences. Narrow tax bases are non-neutral, favoring one product or industry over another, and can undermine revenue stability. and excise tax options both result in relatively minor economic trade-offs for the revenue raised, while the economic trade-offs of raising marginal income tax rates are much harsher.
As a result, a less economically harmful option like eliminating the ESI exclusion results in a much more powerful reduction in long-run debt as a share of GDP. However, even with substantially higher tax revenues, long-run debt-to-GDP would still continue to grow, showing that spending needs to be the primary focus to successfully reduce debt.
That brings us to the options currently on the table. Unfortunately, President Biden’s plan to reduce the deficit, as described in his budget, depends entirely on net revenue increases from raising economically damaging taxes—an approach inconsistent with successful efforts to reduce debt.
The Biden administration’s estimates of nearly $3 trillion in deficit reduction under the budget are highly uncertain, particularly as they depend on a novel set of tax increases. On a conventional basis, Tax Foundation estimates the President’s budget plan would reduce the 10-year deficit by $2.5 trillion. Because the plan would reduce GDP by 1.3 percent, the deficit reduction drops to $1.9 trillion over 10 years on a dynamic basis.
By 2033, publicly held debt as a share of GDP will reach 118 percent under the baseline. Biden’s budget would reduce it to 112 percent conventionally or 114 percent dynamically. In the long run (by 2053), the plan would reduce debt-to-GDP from 195 percent under the baseline to 174 percent conventionally or 180 percent dynamically.
The smaller improvement on a dynamic basis highlights the importance of minimizing the economic costs of tax hikes and instead seeking efficient sources of revenue. For example, in contrast to Biden’s proposals, Tax Foundation’s Tax Reform Plan for Growth and Opportunity proposes replacing the current corporate income taxA corporate income tax (CIT) is levied by federal and state governments on business profits. Many companies are not subject to the CIT because they are taxed as pass-through businesses, with income reportable under the individual income tax. with a distributed profits tax and the current individual income taxAn individual income tax (or personal income tax) is levied on the wages, salaries, investments, or other forms of income an individual or household earns. The U.S. imposes a progressive income tax where rates increase with income. The Federal Income Tax was established in 1913 with the ratification of the 16th Amendment. Though barely 100 years old, individual income taxes are the largest source of tax revenue in the U.S. with a much broader based flat tax, and reforming estate and capital gains taxes at death. Base broadeners in the plan help offset the costs of the reforms, including eliminating most tax expenditures: the exclusion for employer-sponsored health insurance, all itemized deductions, and many tax credits.
The plan is approximately revenue neutral, but because it raises revenue more efficiently, it increases long-run GDP by about 2.4 percent and reduces long-run debt-to-GDP by about 5 percentage points on a dynamic basis.
In lieu of a fundamental overhaul of the tax system, lawmakers may consider permanence for all or part of the expiring Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) provisions. An across-the-board extension of the individual income tax expirations would be pro-growth but would significantly reduce revenue. Alternatively, lawmakers could build on the TCJA’s reforms to further broaden the base by, for example, using the options outlined in Tax Foundation’s Plan for Growth and Opportunity and curtailing new green energy tax credits.
Other reforms, such as permanent expensing for capital investments and research & development, would also enhance the efficiency of the tax system. On a conventional and dynamic basis, such changes would reduce revenue in the short term, but, over the long run, the fading revenue cost and permanent economic benefit would be enough to slightly reduce deficits and the debt-to-GDP ratio.
Lawmakers have a tough task ahead as they consider solutions to stabilize the deficit and debt. Though it may not be politically popular to raise the gas taxA gas tax is commonly used to describe the variety of taxes levied on gasoline at both the federal and state levels, to provide funds for highway repair and maintenance, as well as for other government infrastructure projects. These taxes are levied in a few ways, including per-gallon excise taxes, excise taxes imposed on wholesalers, and general sales taxes that apply to the purchase of gasoline. or broaden the tax baseThe tax base is the total amount of income, property, assets, consumption, transactions, or other economic activity subject to taxation by a tax authority. A narrow tax base is non-neutral and inefficient. A broad tax base reduces tax administration costs and allows more revenue to be raised at lower rates. , to the extent that a comprehensive deficit reduction package includes modest tax increases, such options are the most advisable on economic grounds. Ultimately, a better-designed tax system should be a goal of any fiscal consolidation package.
Related Resources:
This blog post is the third in a series in which our experts explore the issues and potential solutions for America’s growing debt and deficits.
- Fast Approaching Debt Limit Deadline and Growing Debt Demand Action
- How America’s Debt Problem Compares to Other Countries—and Why It Matters
- Tackling America’s Debt & Deficit Crisis Requires Social Security & Medicare Reform
- Debt Ceiling Deal Reduces Deficits in the Short Term But Delays a More Comprehensive Budget Reckoning
- Testimony: Taxes, Spending, and Addressing the U.S. Debt Crisis