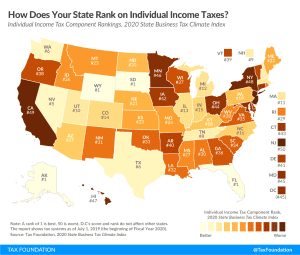
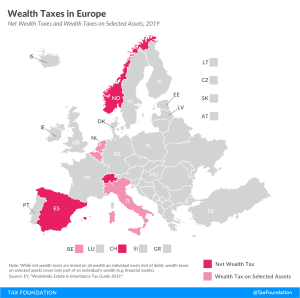
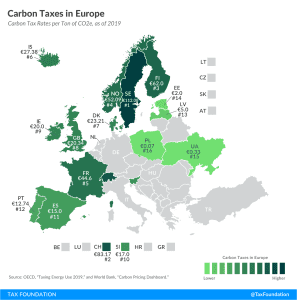
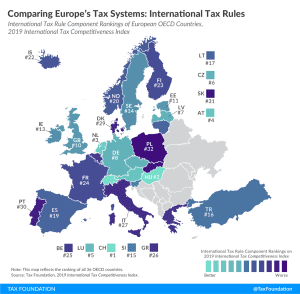
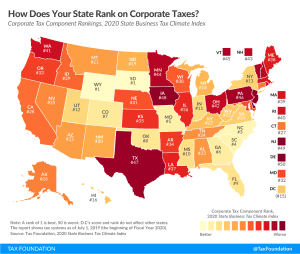
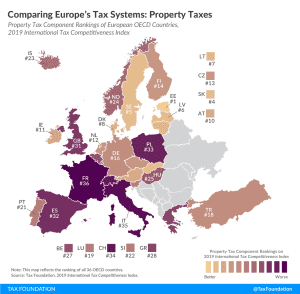
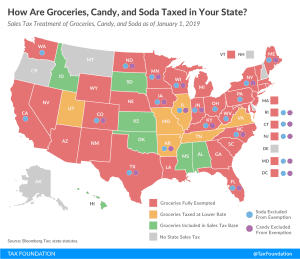
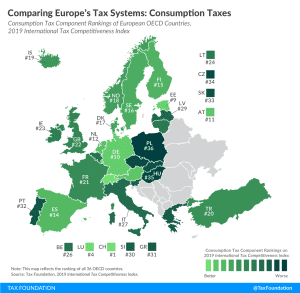
GILTI and Other Conformity Issues Still Loom for States in 2020
Even two years after enactment of the federal Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), many states have yet to issue guidance explaining how they conform to key provisions of the law, particularly those pertaining to international income.
27 min read