All Related Articles

How Do Transfers and Progressive Taxes Affect the Distribution of Income?
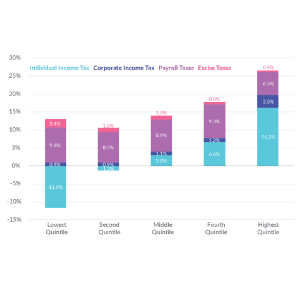
Federal tax rates vary by income group and tax source. The federal tax system redistributes income from high- and low-income taxpayers.
3 min read
Who Benefits from Itemized Deductions?
While some tax preferences like the earned income tax credit (EITC) and child tax credit benefit lower- and middle-income households, others, like itemized deductions, benefit high-income households.
4 min read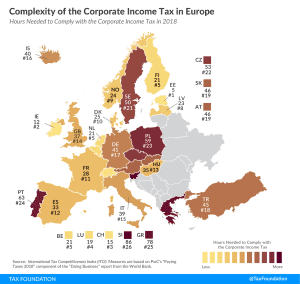

The Top 1 Percent’s Tax Rates Over Time
In the 1950s, when the top marginal income tax rate reached 92 percent, the top 1 percent of taxpayers paid an effective rate of only 16.9 percent. As top marginal rates have fallen, the tax burden on the rich has risen.
5 min read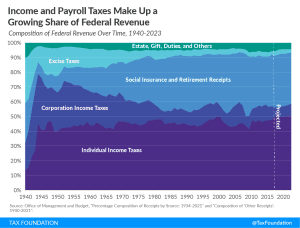
The Composition of Federal Revenue Has Changed Over Time
The federal income tax and federal payroll tax make up a growing share of federal revenue. Individual income taxes have become a central pillar of the federal revenue system, now comprising nearly half of all revenue.
2 min read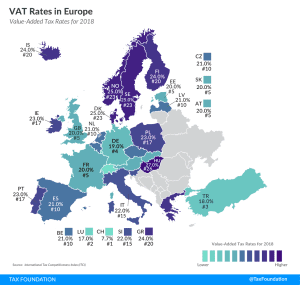
VAT Rates in Europe, 2019
4 min read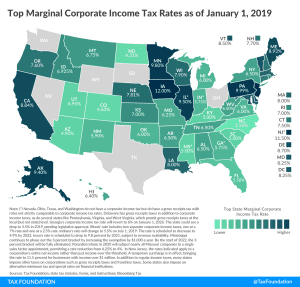
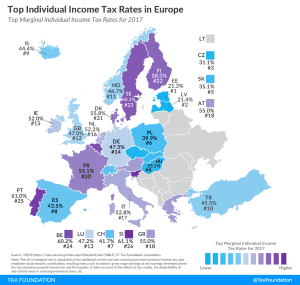

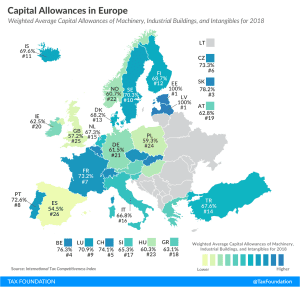
Capital Allowances in Europe, 2019
3 min read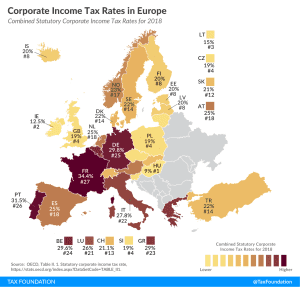

Income Taxes on the Top 0.1 Percent Weren’t Much Higher in the 1950s
Recent plans to increase the tax burden on wealthy Americans, such as higher marginal income tax rates and wealth taxes, are flawed in several ways, including in their lack of understanding of tax history.
4 min read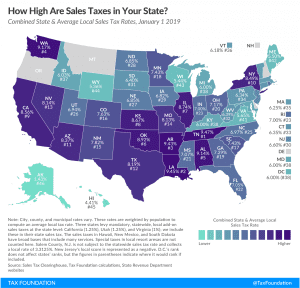
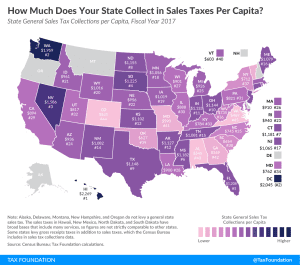
State and Local Sales Tax Rates, 2019
11 min read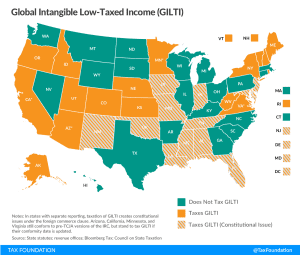
GILTI Minds: Why Some States Want to Tax International Income—And Why They Shouldn’t
The new federal tax on Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income (GILTI) is something of a misnomer: it’s certainly global and it’s definitely income, but the rest of it is, at best, an approximation. It’s not exclusively levied on low-taxed income, nor just on the economic returns from intangible property. So what is GILTI, why might states tax it, and what’s the problem with that?
8 min readToward a State of Conformity: State Tax Codes a Year After Federal Tax Reform
States incorporate provisions of the federal tax code into their own codes in varying degrees, meaning that federal tax reform has implications for state revenue beyond any broader economic effects of tax reform.
73 min read