A marriage penalty is when a household’s overall tax bill increases due to a couple marrying and filing taxes jointly. A marriage penalty typically occurs when two individuals with similar incomes marry; this is true for both high- and low-income couples.
Federal Marriage Penalty
Prior to the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) of 2017, the marriage penalty was especially pronounced for medium- to high-income earners because the income tax brackets for married couples at the top of the income tax schedule were not twice as wide as the equivalent brackets for single individuals. Currently, however, all tax brackets for married filers are exactly double those for single filers, except for the top 37 percent marginal rate, in which case the tax bracket for married filers is just 20 percent wider than for single filers. As such, marriage penalties at the federal level are generally only felt at very high income levels.
| Tax Rate | For Single Filers | For Married Individuals Filing Joint Returns | For Heads of Households |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | $0 to $11,000 | $0 to $22,000 | $0 to $15,700 |
| 12% | $11,000 to $44,725 | $22,000 to $89,450 | $15,700 to $59,850 |
| 22% | $44,725 to $95,375 | $89,450 to $190,750 | $59,850 to $95,350 |
| 24% | $95,375 to $182,100 | $190,750 to $364,200 | $95,350 to $182,100 |
| 32% | $182,100 to $231,250 | $364,200 to $462,500 | $182,100 to $231,250 |
| 35% | $231,250 to $578,125 | $462,500 to $693,750 | $231,250 to $578,100 |
| 37% | $578,125 or more | $693,750 or more | $578,100 or more |
| Source: Internal Revenue Service | |||
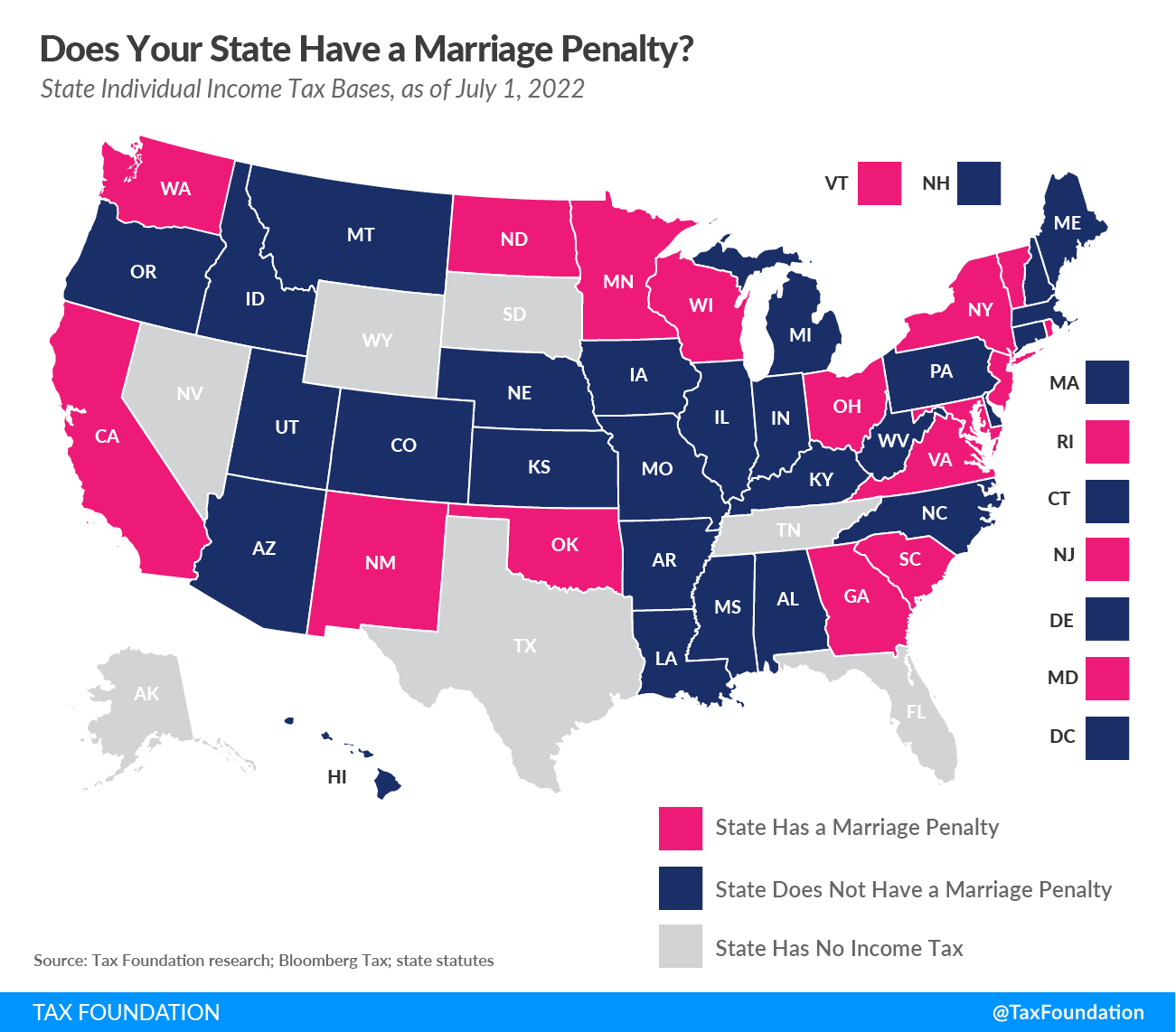
State Marriage Penalty
On the state level, marriage penalties occur when income tax brackets for married taxpayers filing jointly are less than double the bracket widths that apply to single filers. In other words, married couples who file jointly under this scenario face a higher effective tax rate than they would if they filed as two single individuals with the same amount of combined income.
This non-neutral tax treatment is particularly harmful to owners of pass-through businesses, who pay taxes on their business income under the individual income tax system. Under a marriage penalty, married business owners are subject to higher effective tax rates on their business income than they would be otherwise.
Fifteen states (displayed in pink on the map below) have a marriage penalty built into their bracket structure. Seven additional states (Arkansas, Delaware, Iowa, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, and West Virginia), as well as the District of Columbia, offset the marriage penalty in their bracket structure by allowing married taxpayers to file separately on the same return to avoid losing credits and exemptions available to joint filers or which cannot be allocated among filers (for instance, child tax credits). Ten states have a graduated-rate income tax but double their brackets to avoid a marriage penalty: Alabama, Arizona, Connecticut, Hawaii, Idaho, Kansas, Louisiana, Maine, Nebraska, and Oregon.
Stay updated on the latest educational resources.
Level-up your tax knowledge with free educational resources—primers, glossary terms, videos, and more—delivered monthly.
Subscribe