The individual income taxAn individual income tax (or personal income tax) is levied on the wages, salaries, investments, or other forms of income an individual or household earns. The U.S. imposes a progressive income tax where rates increase with income. The Federal Income Tax was established in 1913 with the ratification of the 16th Amendment. Though barely 100 years old, individual income taxes are the largest source of tax revenue in the U.S. is one of the most significant sources of revenue for state and local governments. In fiscal year 2018, the most recent year for which data are available, individual income taxes generated 24.2 percent of state and local taxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities. collections, just ahead of general sales taxes (23.3 percent).
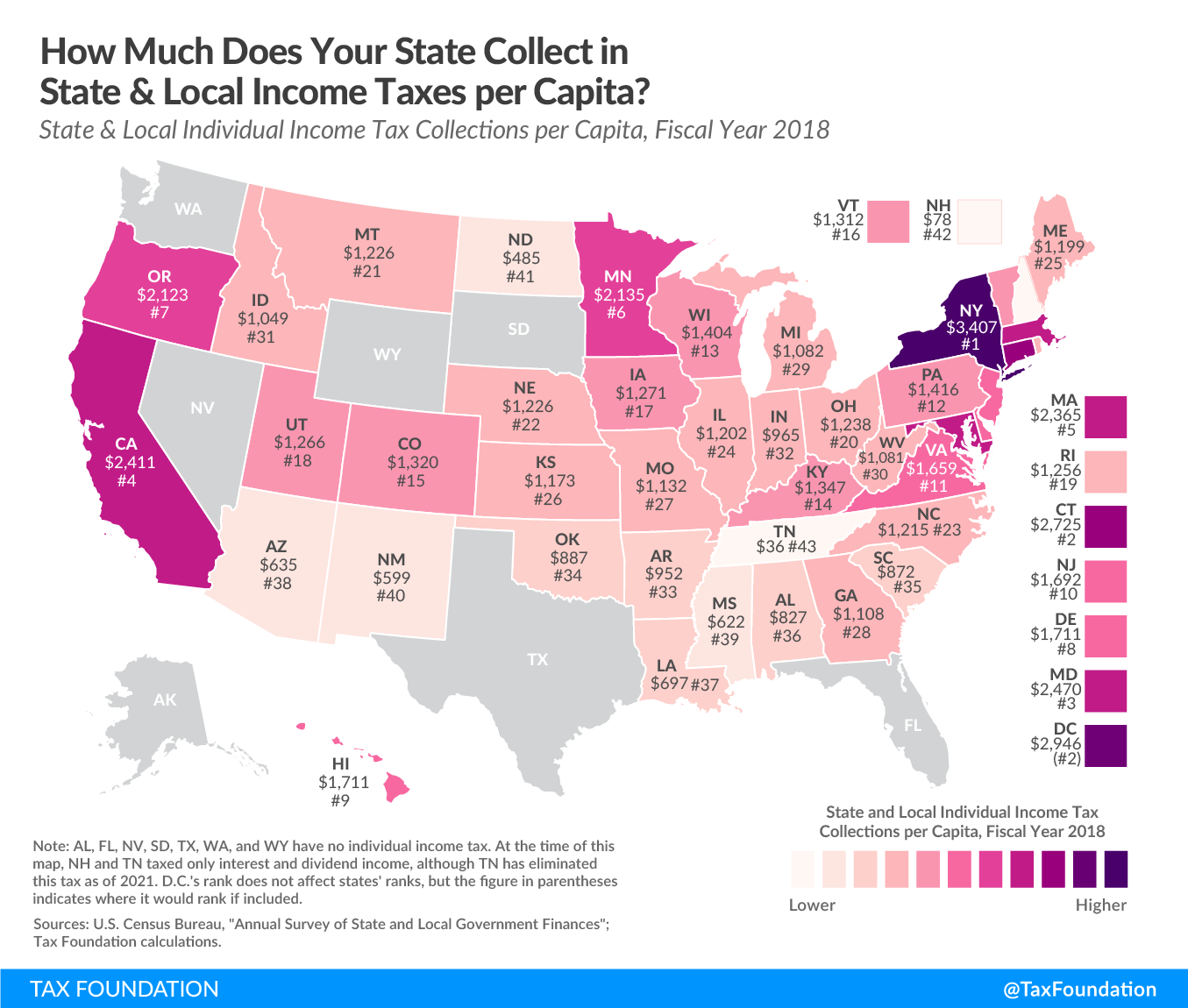
The following map shows combined state and local individual income tax collections per capita for each state in fiscal year 2018. As of that year, 41 states and the District of Columbia levied broad-based taxes on wage income and investment income, while two states—New Hampshire and Tennessee—taxed investment income but not wage income. Tennessee’s tax on investment income—known as the “Hall tax”—was fully repealed as of January 2021. In all, eight states forgo an individual income tax: Alaska, Florida, Nevada, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Washington, and Wyoming.
On average, state and local governments collected $1,303 per capita in individual income taxes, but collections varied widely from state to state. This was a function of both rate structures and income distributions, with higher-income states generating significantly more revenue per capita whether they had a high graduated rate system, like California, or a modest flat-rate income tax, like Massachusetts.
New York ($3,407), the District of Columbia ($2,946), Connecticut ($2,725), Maryland ($2,470), California ($2,411), and Massachusetts ($2,365) came in with the top collections per capita. Tennessee ($36) and New Hampshire ($78) taxed investment income but not wage income, making them the states with the lowest individual income tax collections per capita. Of the states that tax wage income, the lowest collections per capita in fiscal year 2018 were in North Dakota ($485), New Mexico ($599), Mississippi ($622), Arizona ($635), and Louisiana ($697).
Note: This map is part of a series on state and local tax collections per capita.
Facts and Figures: How Does Your State Compare?
Stay informed on the tax policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted experts delivered straight to your inbox.
Subscribe