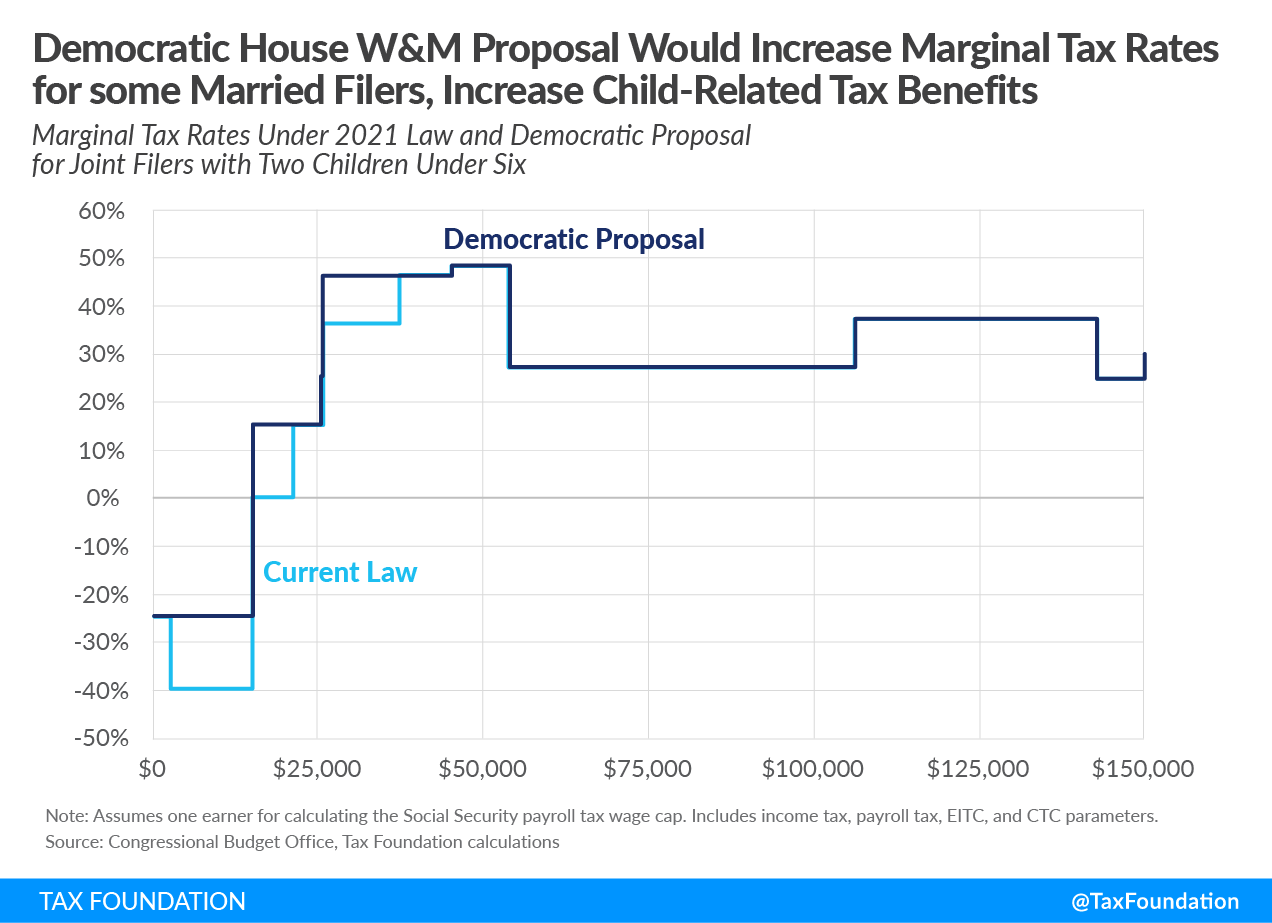
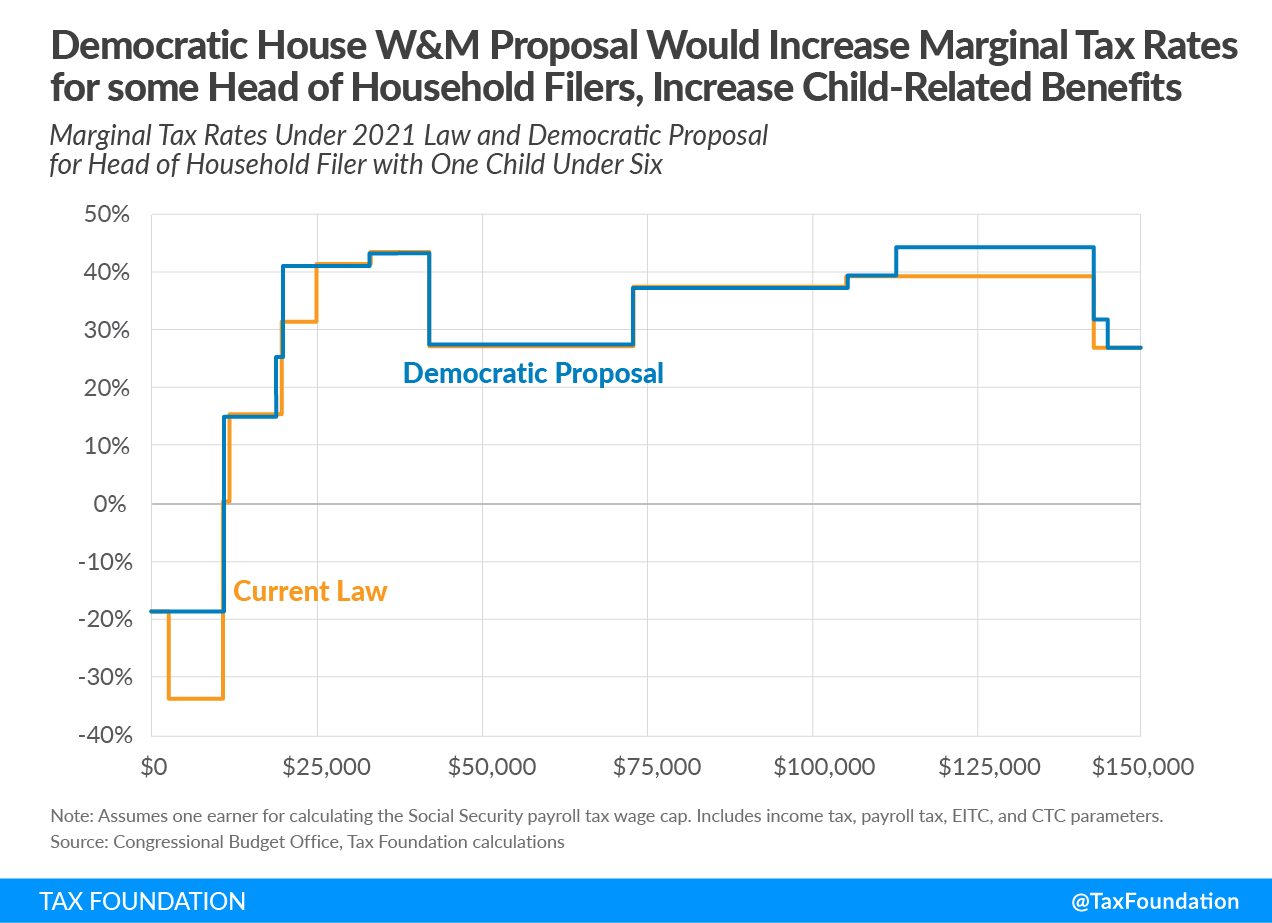
The coronavirus relief legislation passed out of the House Ways and Means CommitteeThe Committee on Ways and Means, more commonly referred to as the House Ways and Means Committee, is one of 29 U.S. House of Representative committees and is the chief tax-writing committee in the U.S. The House Ways and Means Committee has jurisdiction over all bills relating to taxes and other revenue generation, as well as spending programs like Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment insurance, among others. last week would significantly expand the child tax creditA tax credit is a provision that reduces a taxpayer’s final tax bill, dollar-for-dollar. A tax credit differs from deductions and exemptions, which reduce taxable income, rather than the taxpayer’s tax bill directly. (CTC) for 2021, from its current $2,000 maximum to a fully refundable $3,600 for children 6 and under and $3,000 for children over 6. Monthly payments would be provided based on income taxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities. returns on file with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) for 2019 or 2020.
The changes would increase the benefits that lower-income households receive by making the CTC fully refundable and eliminating the phase-in with earned income. While overall benefits would increase, eliminating the phase-in would also affect marginal tax rates. Marginal tax rates on labor income measure the effective tax rate that applies to earning one more dollar of income and can differ from statutory individual income taxAn individual income tax (or personal income tax) is levied on the wages, salaries, investments, or other forms of income an individual or household earns. The U.S. imposes a progressive income tax where rates increase with income. The Federal Income Tax was established in 1913 with the ratification of the 16th Amendment. Though barely 100 years old, individual income taxes are the largest source of tax revenue in the U.S. rates due to phase-ins and phaseouts of various tax provisions as well as payroll taxA payroll tax is a tax paid on the wages and salaries of employees to finance social insurance programs like Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment insurance. Payroll taxes are social insurance taxes that comprise 24.8 percent of combined federal, state, and local government revenue, the second largest source of that combined tax revenue. es and other taxes on income.
Examining marginal tax rateThe marginal tax rate is the amount of additional tax paid for every additional dollar earned as income. The average tax rate is the total tax paid divided by total income earned. A 10 percent marginal tax rate means that 10 cents of every next dollar earned would be taken as tax. s can help show the incentives that workers face and how policies influence labor supply. We can see how the tax code would treat an additional dollar of income earned under the expanded child tax credit compared to current law.
Take, for example, a household with married taxpayers filing jointly and two children under 6. Under the proposal, their maximum CTC of $4,000 under current law would rise to a maximum of $7,200 under the Democratic proposal. The overall benefit would significantly increase. But under the proposal, households would see an increase in marginal tax rates because the CTC no longer phases in and because of the phaseout of the larger CTC benefit.
Under current law, the credit phases in with earned income above $2,500 at a 15 percent rate, which reduces marginal tax rates by 15 percentage points over the phase-in range. Because the newly proposed credit provides the full amount immediately to households, it no longer has a phase-in and therefore no longer reduces marginal tax rates for lower-income households (see Figure 1). The result is higher marginal tax rates over the current law phase-in range.
The Democratic proposal would also increase marginal tax rates for households at higher income levels by phasing out the extra benefit that the proposal provides over current law. The extra credit provided under the proposal (in the current example, an extra $3,200 above the current law amount of $4,000) would begin phasing out at $150,000 in income at a 5 percent rate until it reaches the amount that would be provided under current law, to preserve existing CTC benefits. The phaseout of the extra amount increases marginal tax rates by 5 percentage points compared to current law (see Figure 1).
Marginal tax rates would change in a similar way for other filers. For example, a single parent with one child under 6 (a head of household filer) would be eligible for a maximum $2,000 CTC under current law compared to $3,600 under the Democratic proposal. Like the previous example, marginal tax rates would be higher because the CTC no longer phases in and because of the phaseout of the additional CTC benefit.
The proposed expansion of credits is only for 2021 and would not be a permanent policy change. Other proposals, like Senator Mitt Romney’s (R-UT) Family Security Act, would permanently expand the child tax credit. It is likely that any temporary expansion would create pressure for an extension or permanence, however. Some argue that the increases in marginal tax rates created by removing the phase-ins would reduce work incentives and potentially negate the positive effects of larger benefits; but the magnitude of the effect is debated. Comparing both the total amount of benefits and the changes in marginal tax rates under each proposal can inform policymakers of potential trade-offs as they work to reform child- and work-related benefits.
Related Resources
Stay informed on the tax policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted experts delivered straight to your inbox.
SubscribeStay informed on the tax policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted experts delivered straight to your inbox.
Subscribe