A recent report on taxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities. revenue sources shows the extent to which the United States and other OECD countries rely on different taxes for government revenues. Policy and economic differences among OECD countries have created variances in how they raise tax revenue, with the United States deviating substantially from the OECD average on some sources of revenue.
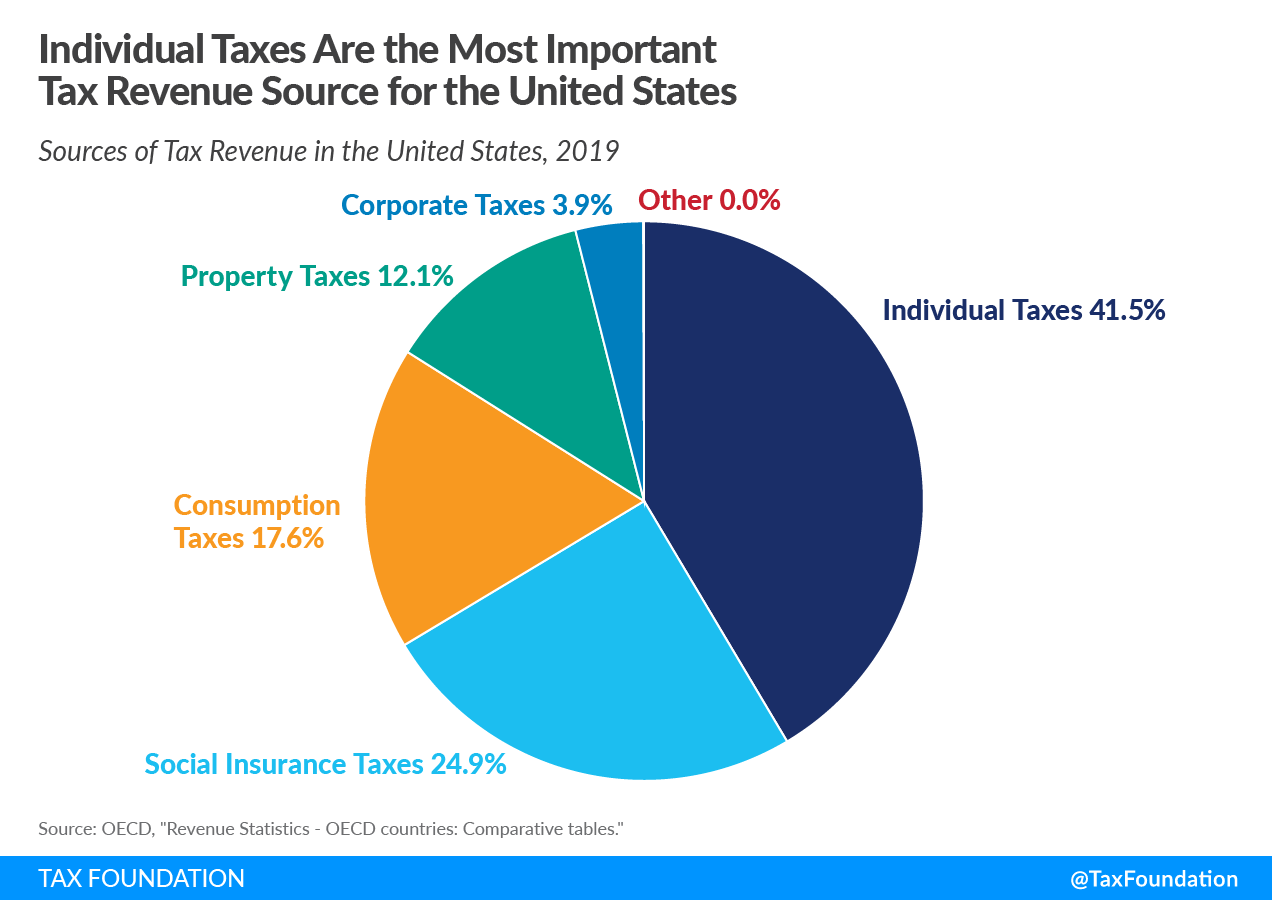
In the United States, individual income taxes (federal, state, and local) were the primary source of tax revenue in 2019, at 41.5 percent of total tax revenue. Social insurance taxes made up the second-largest share, at 24.9 percent, followed by consumption taxes, at 17.6 percent, and property taxes, at 12.1 percent. Corporate income taxes accounted for 3.9 percent of total tax revenue in 2019, the second year after passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, and 1.9 percentage points less than in 2017.
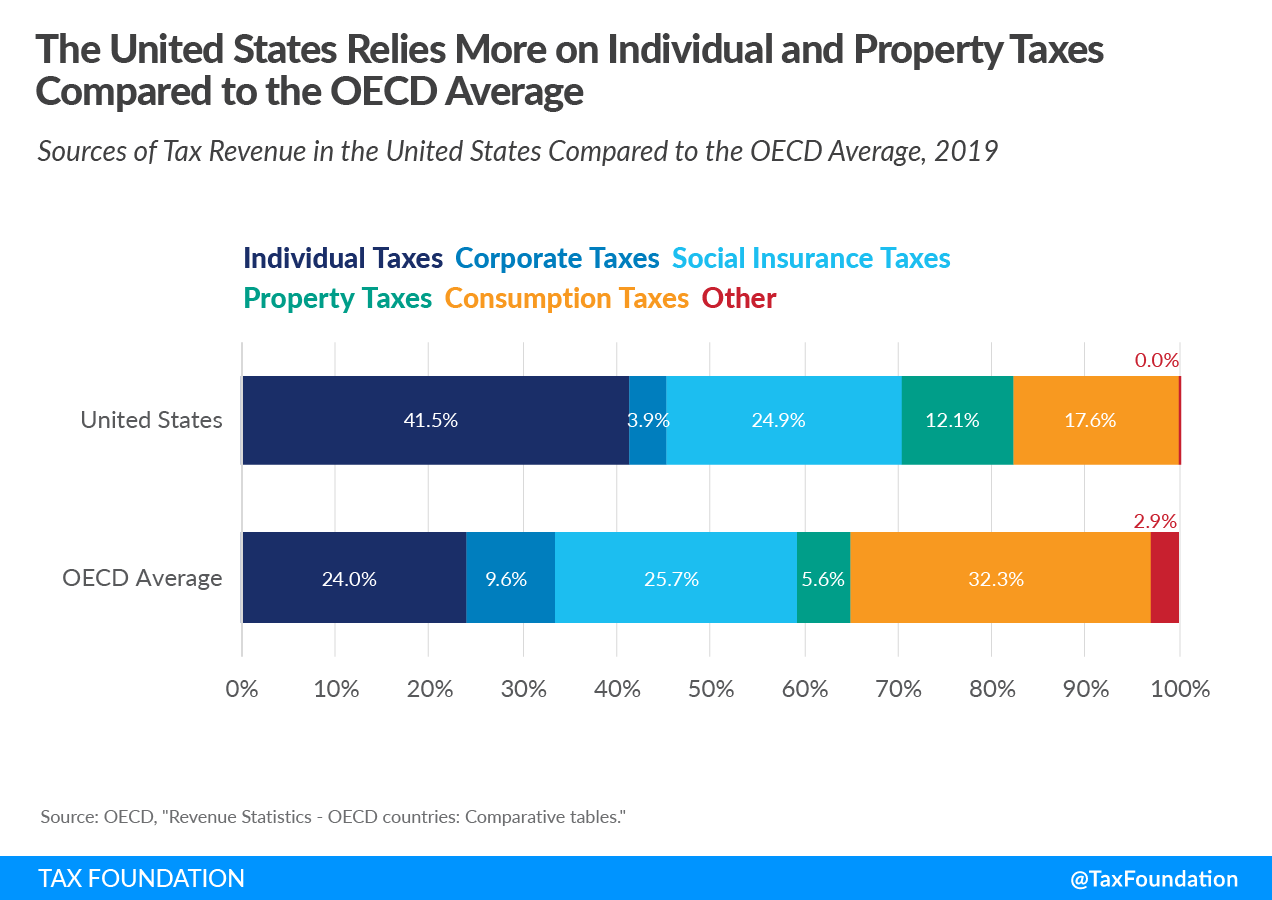
Compared to the OECD average, the United States relies significantly more on individual income taxes and property taxes. While OECD countries on average raised 24 percent of total tax revenue from individual income taxes, the share in the United States was 41.5 percent, a difference of 17.5 percentage points. This is partially because more than half of business income in the United States is reported on individual tax returns. OECD countries on average raised 5.6 percent of total tax revenue from property taxes, compared to 12.1 percent in the United States.
The United States relies much less on consumption taxes than other OECD countries. Taxes on goods and services accounted for only 17.6 percent of total tax revenue in the United States, compared to 32.3 percent in the OECD. This is because all OECD countries, except the United States, levy value-added taxes (VAT) at relatively high rates. State and local sales taxA sales tax is levied on retail sales of goods and services and, ideally, should apply to all final consumption with few exemptions. Many governments exempt goods like groceries; base broadening, such as including groceries, could keep rates lower. A sales tax should exempt business-to-business transactions which, when taxed, cause tax pyramiding. rates in the United States are relatively low by comparison.
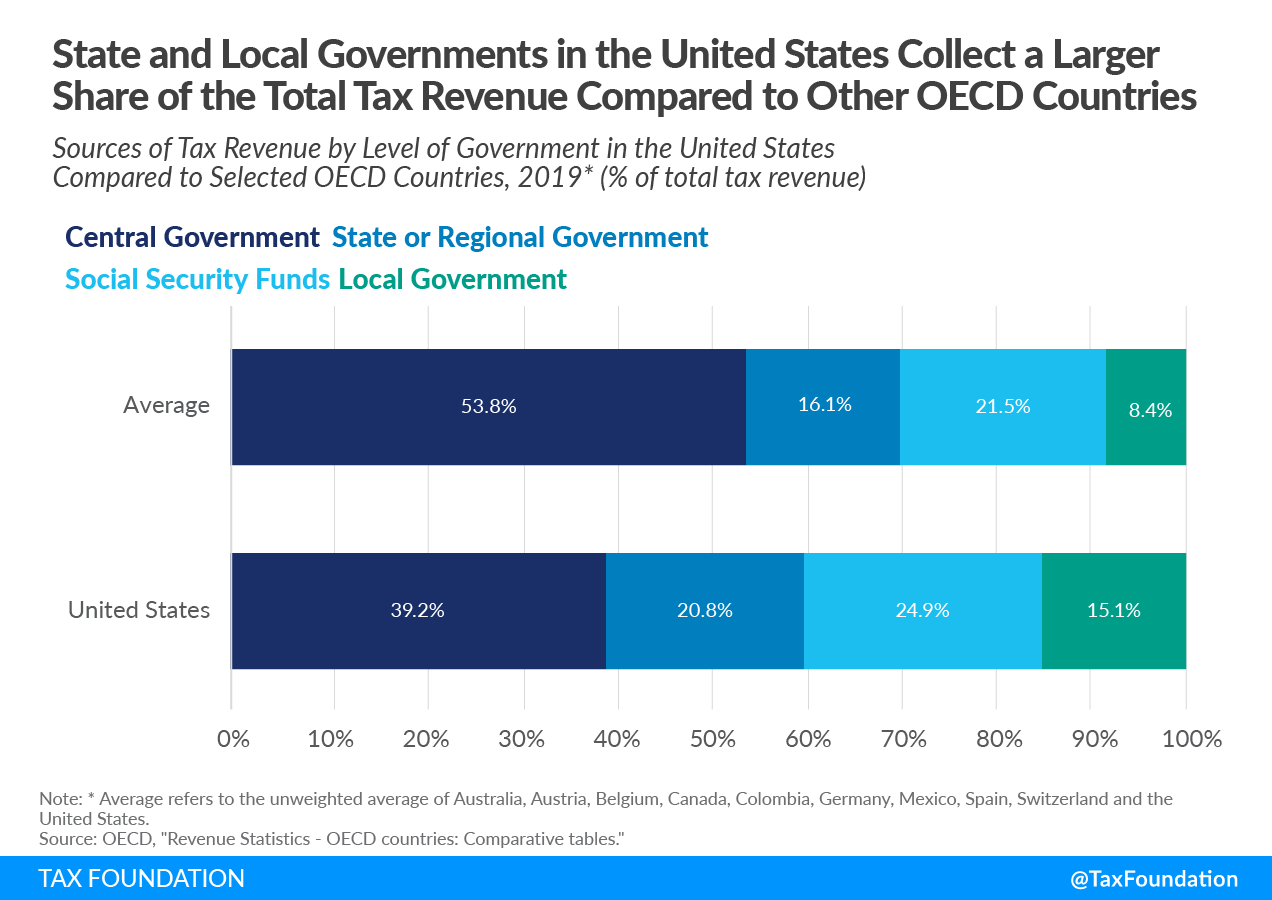
When looking at the sources of tax revenue by level of government, in 2019, the federal government of the United States collected the largest share of tax revenue, at 39.2 percent of total tax revenue. Social Security funds collected the second-highest share of revenue at 24.9 percent. State government collected 20.8 percent and local government accounted for 15.1 percent of the total revenue.
Compared to nine other federal countries and countries with a highly decentralized political structure, state and local governments in the United States collected a larger share of revenues. The state or regional governments of the OECD countries analyzed collected, on average, 16 percent of total tax revenue, while the state governments in the United States collected 20.8 percent. On the other hand, the local governments of the other fiscally decentralized OECD countries collected, on average, 8.4 percent of the total tax revenue, compared to 15.1 percent in the United States. The United States also collected more through the Social Security funds than the selected OECD countries. On average, the central governments of the fiscally decentralized OECD countries collected 53.8 percent of the total tax revenue, 14.6 percentage points more than the federal government of the United States.
Every country’s mix of taxes is different, depending on factors such as its economic situation and policy goals. However, each type of tax impacts the economy in a different way, with some taxes being more adverse than others. Generally, consumption-based taxes are a more efficient source of revenue because they create less economic damage and distortionary effects than taxes on income. Countries also have different levels of governments at which taxes are collected. The United States along with nine other OECD countries has a decentralized political structure where state or regional governments play an important role in the tax collection. Nearly half of tax revenues in the United States is raised at the state and local level.
Share this article