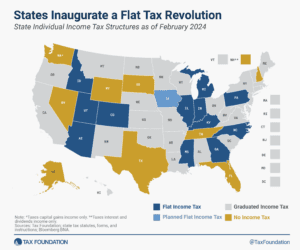
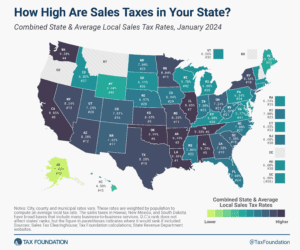
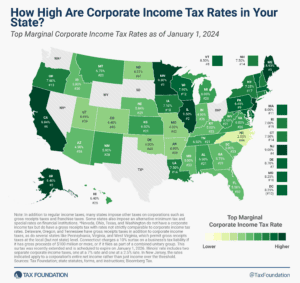
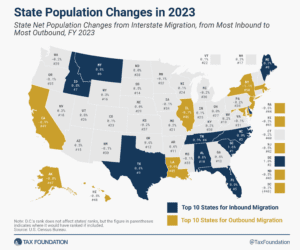
The State Flat Tax Revolution: Where Things Stand Today
In 2021 and 2022 alone, more states enacted laws converting graduated-rate individual income tax structures into single-rate income tax structures than did so in the whole 108-year history of state income taxation up until that point.
10 min read