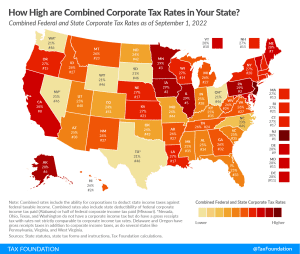
Combined Federal and State Corporate Income Tax Rates in 2022
When examining tax burdens on businesses, it is important to consider both federal and state corporate taxes. Corporate taxes are one of the most economically damaging ways to raise revenue and are a promising area of reform for states to increase competitiveness and promote economic growth, benefiting both companies and workers.
2 min read