The economic crisis caused by the coronavirus pandemic poses a triple challenge for tax policy in the United States. Lawmakers are tasked with crafting a policy response that will accelerate the economic recovery, reduce the mounting deficit, and protect the most vulnerable.
To assist lawmakers in navigating the challenge, and to help the American public understand the tax changes being proposed, the Tax Foundation’s Center for Federal Tax Policy modeled how 70 potential changes to the tax code would affect the U.S. economy, distribution of the tax burden, and federal revenue.
In tax policy there is an ever-present trade-off among how much revenue a tax will raise, who bears the burden of a tax, and what impact a tax will have on economic growth. Armed with the information in our new book, Options for Reforming America’s Tax Code 2.0, policymakers can debate the relative merits and trade-offs of each option to improve the tax code in a post-pandemic world.
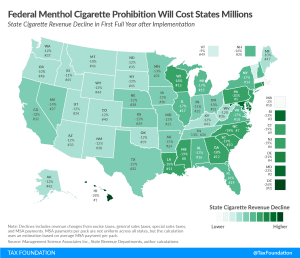
Federal Menthol Cigarette Ban May Cost Governments $6.6 Billion
The FDA’s expected announcement of a national ban on menthol-flavored cigarettes and cigars with a characterizing flavor would carry significant revenue implications for both the federal government and state governments, with likely limited benefits in smoking cessation.
6 min read
The Global Minimum Tax Changes the Game for Build Back Better Revenue
One goal for the Build Back Better Act has been to increase the amount of revenue the U.S. raises from U.S. companies at home or abroad. With the global minimum tax rules in play, it is likely that the expected gains to the U.S. Treasury from foreign profits of U.S. companies will diminish.
5 min read
Rushing Headlong into Formulary Apportionment
Complex tax policies that work well “in theory” can often have a hard time when the rubber meets the road. One instance of this is the challenge that the OECD has created for itself with the global tax deal, also fondly known as Pillar 1 and Pillar 2.
7 min read
Federal Gas Tax Holiday? Suspending the Gas Tax Is a Mistake
If policymakers are looking to change the tax code to help fight inflation, they should pump the brakes on the federal gas tax holiday and instead consider structural reforms to raise the economy’s productive capacity in the long term.
4 min read
Proposal to Rid Ohio of Gross Receipt Taxes
A group of lawmakers in Ohio have proposed to repeal the state’s gross receipt tax (GRT), also known as the commercial activity tax (CAT).
5 min read
Alabama Should Pursue Permanent, Not Piecemeal, Solutions to Federal Deductibility Issues
Alabama lawmakers are acting to ensure that federal relief from the American Rescue Plan Act does not increase tax liabilities in the state.
4 min read
Large Spread in Tax Treatment of Sports Betting Operators
Since 2018, 30 states and the District and Columbia have legalized and imposed taxes on sports betting. States that have yet to legalize, but which may do so, should pay attention to the impact of tax design in states that already have legal and taxed sports betting—specifically tax base design.
8 min read
Massachusetts Should Reject Gross Receipts Taxes
Not only is the tax inequitable and inefficient, it also could be what drives businesses and remote workers into another state.
7 min read
Rate Reductions Would Put Michigan in Top 10
Amid record surpluses, Michigan lawmakers are looking to give relief to taxpayers and enhance the state’s competitive standing.
3 min read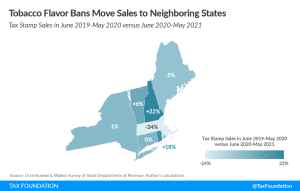
Massachusetts Flavored Tobacco Ban: No Impact on New England Sales
A recent JAMA Internal Medicine study on the impact of the Massachusetts flavored tobacco ban indicates that it has been a success. Unfortunately, it left out a very important piece of information: cross-border trade.
4 min read