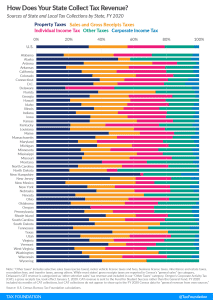
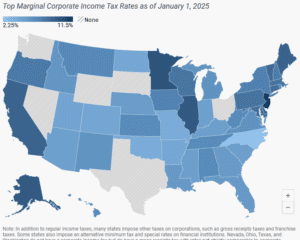
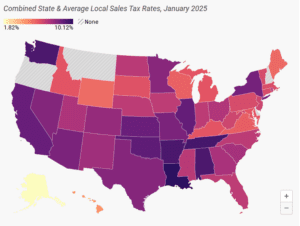
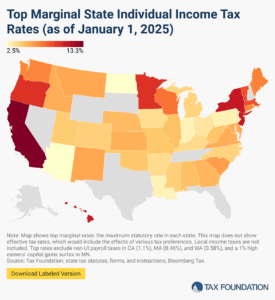
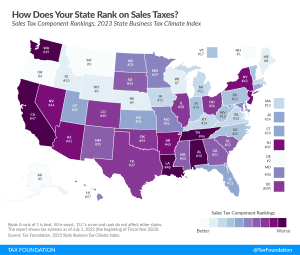
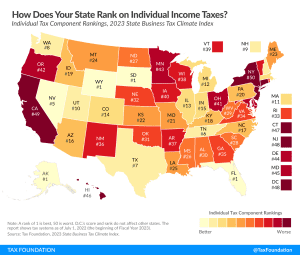
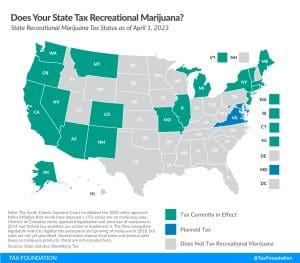
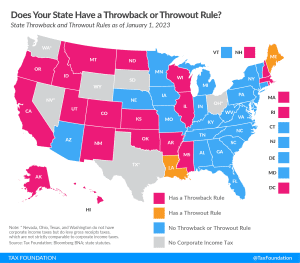
2025 State Tax Competitiveness Index
The State Tax Competitiveness Index enables policymakers, taxpayers, and business leaders to gauge how their states’ tax systems compare. While there are many ways to show how much state governments collect in taxes, the Index evaluates how well states structure their tax systems and provides a road map for improvement.
115 min read