Wednesday, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) published its annual analysis of the distribution of American household incomes and taxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities. burdens, this time for 2018, the year after the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) was enacted. CBO data shows that the TCJA reduced federal tax rates for households across every income level while increasing the share of tax paid by the top 1 percent. Showing how the TCJA impacted household taxes is important to consider as policymakers debate whether to reverse key aspects of the 2017 tax law.
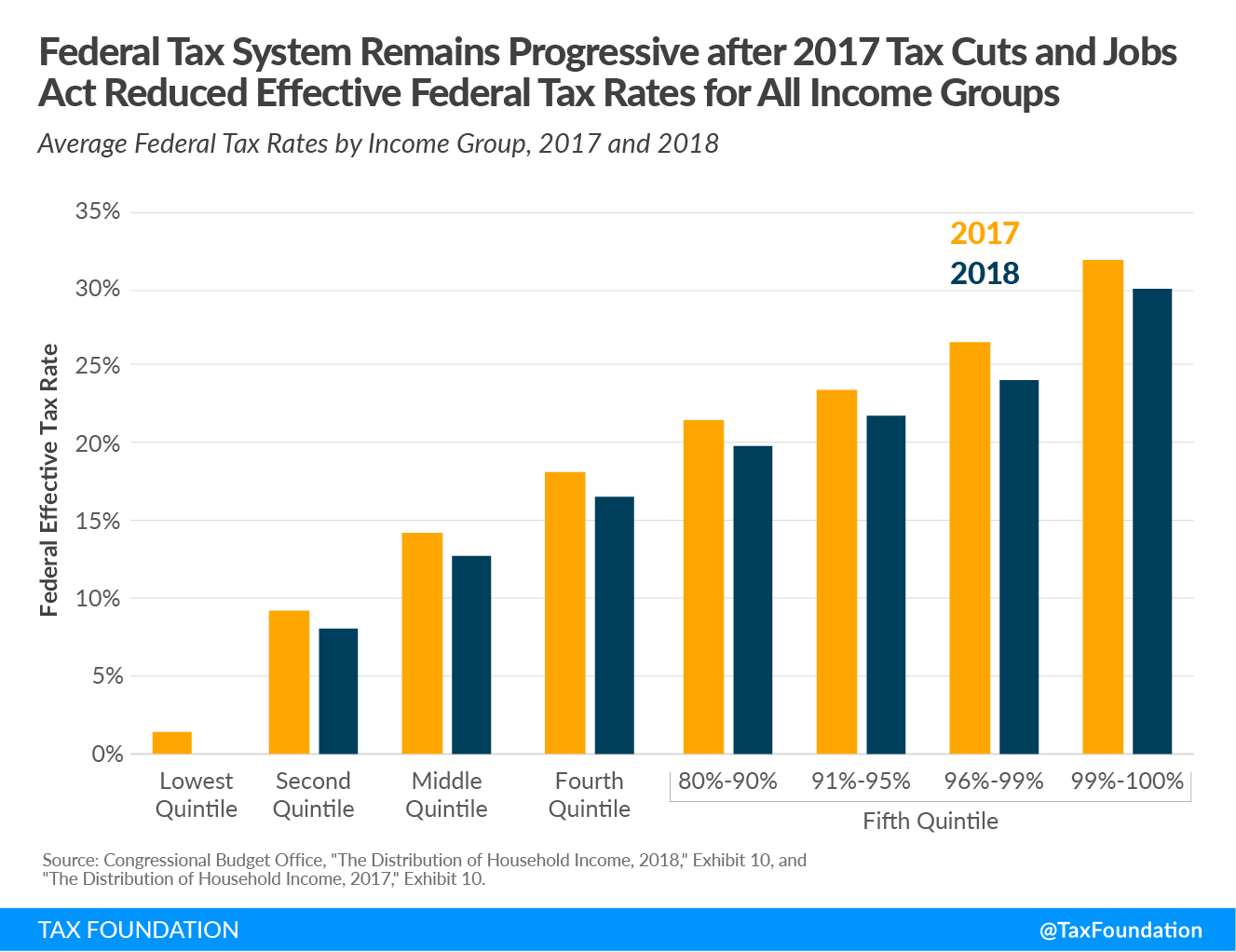
CBO found that average federal tax rates fell for households across the board because of the TCJA’s individual income taxAn individual income tax (or personal income tax) is levied on the wages, salaries, investments, or other forms of income an individual or household earns. The U.S. imposes a progressive income tax where rates increase with income. The Federal Income Tax was established in 1913 with the ratification of the 16th Amendment. Though barely 100 years old, individual income taxes are the largest source of tax revenue in the U.S. provisions, including the doubled standard deduction from $12,400 to $24,800, reduced income tax rates, and expanded child tax credit (CTC). High-earning households saw a reduction in their effective tax rates primarily from the corporate tax rate dropping from 35 percent to 21 percent and tax reductions for pass-through firms.
The TCJA reduced the average federal tax rate from 20.8 percent to 19.3 percent for all filers. The bottom 20 percent of earners saw their average federal tax rate fall from 1.2 percent to nearly 0 percent. The top 1 percent of filers saw a 1.5 percentage point decline, from 31.7 percent in 2017 to 30.2 percent in 2018.
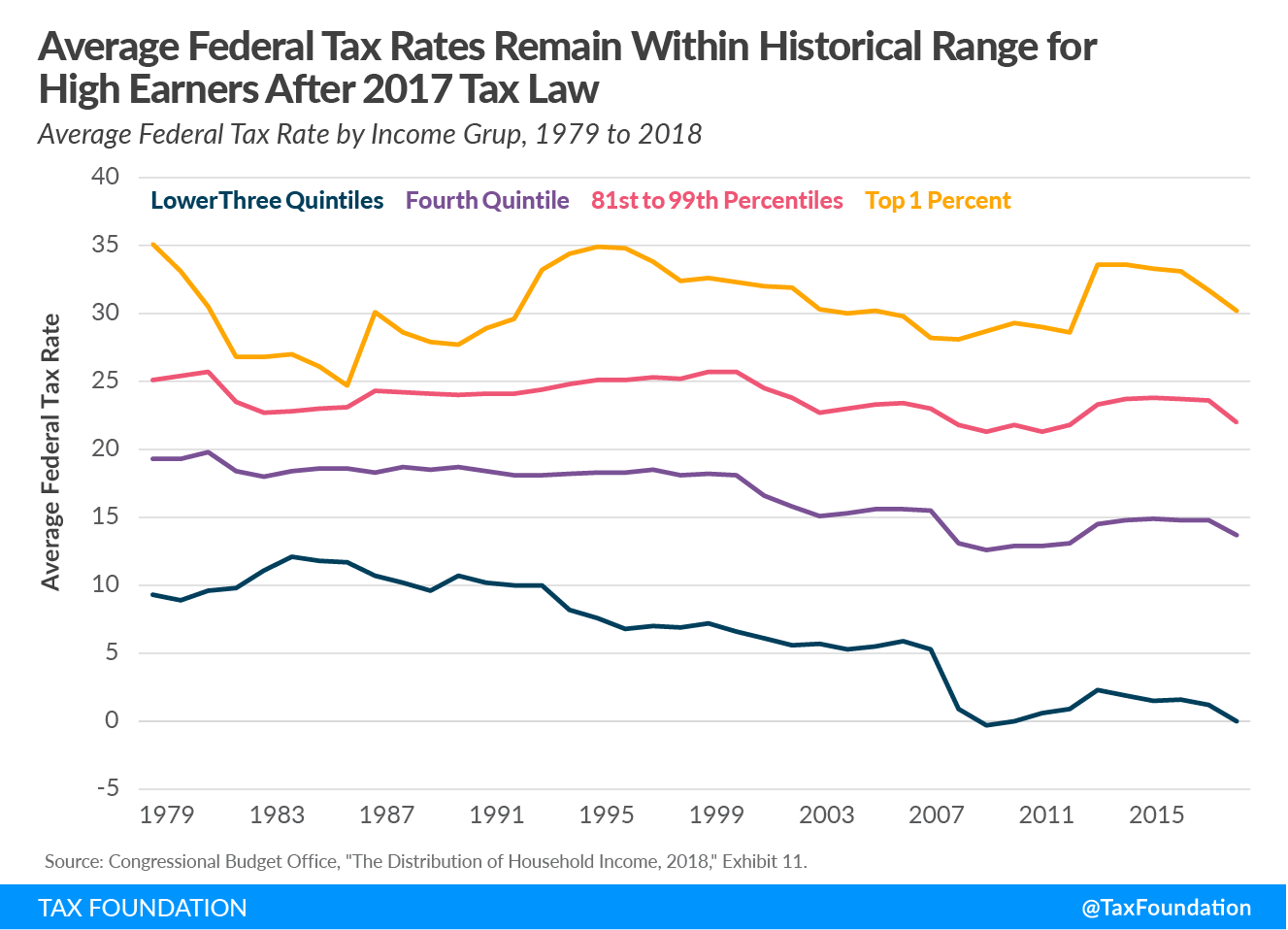
CBO data also shows that average tax rates remained within their historical ranges in 2018. The top 1 percent’s 30.2 percent average federal tax rate was only slightly below the average for 1979 to 2017 (30.6 percent), and the average rate for the bottom 20 percent in 2018—about 0 percent—is well below its 1979 to 2017 average of 6.6 percent. The near zero rate for the bottom 20 percent is because the expansion in refundable tax credits over the past 40 years has driven down average tax rates for low-income households.
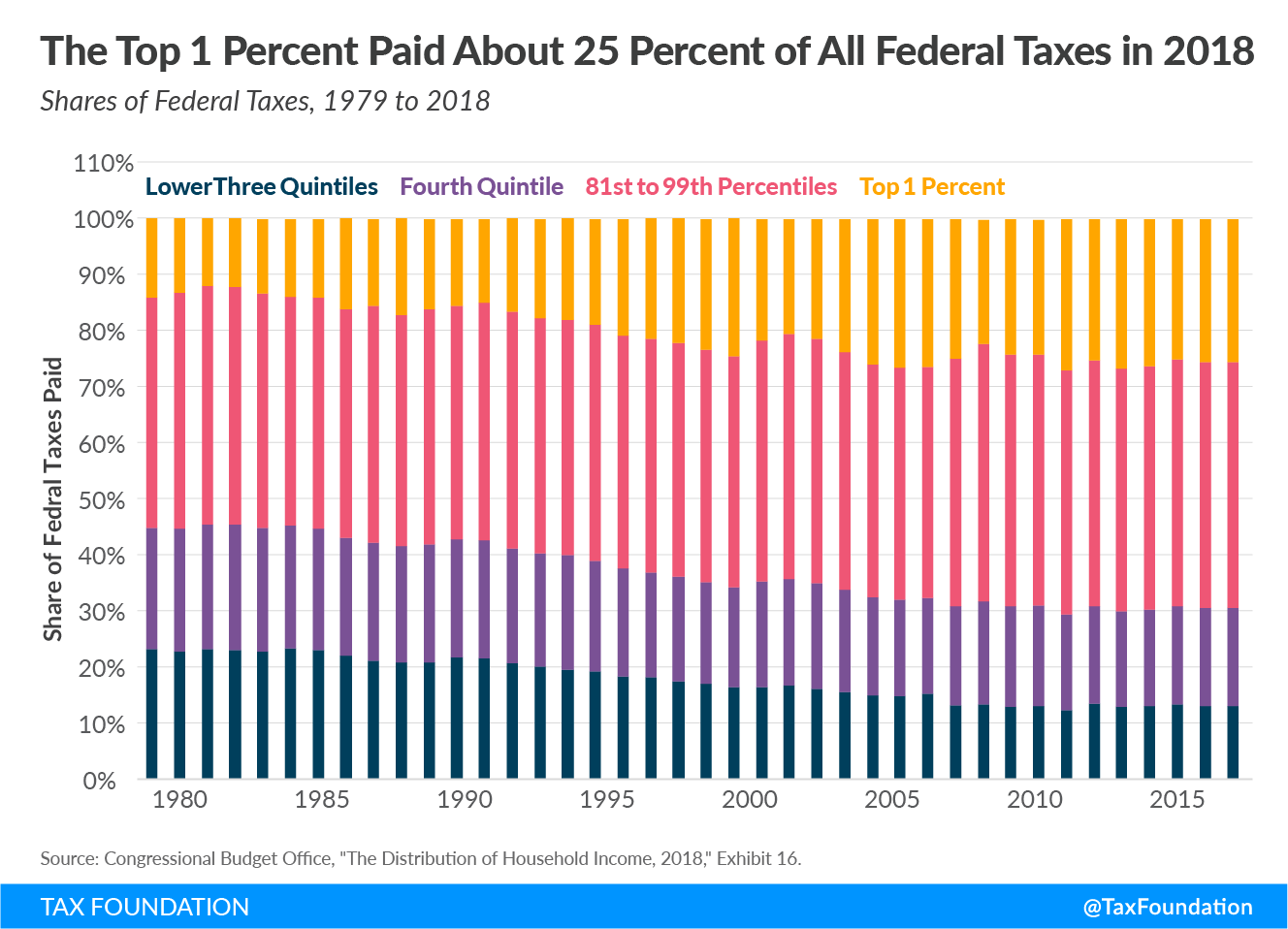
Even though the TCJA reduced household tax rates across the board, the top 1 percent of households saw their share of federal taxes paid increase from 25.5 percent in 2017 to 25.9 percent in 2018. That makes their share in 2018 the highest of federal taxes paid by an income group since 2008 and the third-highest since 1979. By contrast, the bottom 20 percent of households saw a reduction in their share of federal taxes paid, from 13 percent in 2017 to 12.5 percent in 2018.
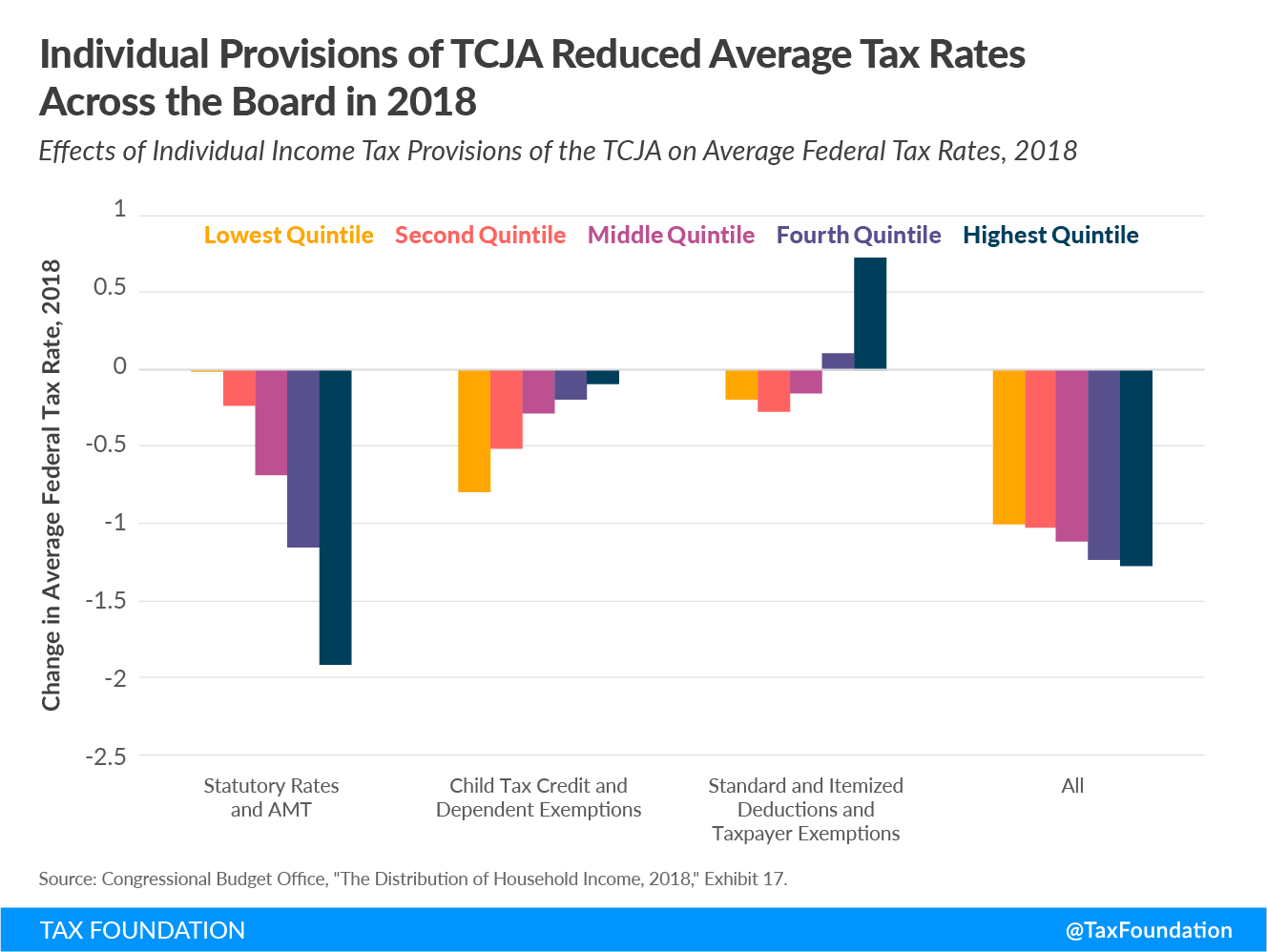
The TCJA’s individual income tax changes had different impacts on households depending on their income level. For example, the reduction in the statutory individual income tax rates and bracket consolidation reduced the federal tax rate paid by the top 20 percent of households by 1.9 percentage points, but reduced the federal tax rate paid by the bottom 20 percent by only 0.01 percentage points. The CTC expansion, on the other hand, benefited the bottom quintile of households by a larger margin, at 0.8 percentage points.
The expansion of the standard deductionThe standard deduction reduces a taxpayer’s taxable income by a set amount determined by the government. It was nearly doubled for all classes of filers by the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) as an incentive for taxpayers not to itemize deductions when filing their federal income taxes. , elimination of taxpayer exemptions, and limitations on itemized deductions such as the $10,000 cap on state and local taxes (SALT) tended to reduce the average federal tax rate paid by the bottom 60 percent of households, but raised the average tax rateThe average tax rate is the total tax paid divided by taxable income. While marginal tax rates show the amount of tax paid on the next dollar earned, average tax rates show the overall share of income paid in taxes. for the top 40 percent of earners. This is because “the increase in the standard deduction was generally larger than the effect of removing the taxpayer exemptions” for lower-income households, while higher-earning households are more likely to itemize their deductions and run into itemized deduction limits. These households tend to have higher marginal tax rates they are deducting against, too, which means they benefit more from those deductions.
Combined, the TCJA’s individual provisions reduced federal tax rates by 1 percent for the bottom income quintile and 1.3 percent for the top 20 percent of households. CBO finds that the overall impact of the TCJA’s individual and corporate tax changes reduced average tax rates by about 1.3 percentage points in 2018. The business provisions within the TCJA reduced the top 20 percent’s federal tax rate by 2.7 percentage points, partially because business income tends to be earned by higher earners.
Share this article