FDA Ban on Flavored Cigars Could Cost $836 Million in Annual Excise Tax Revenue
The FDA’s proposal to ban flavored cigars would carry significant revenue implications for many state governments.
7 min readHow does Washington’s tax code compare? Washington does not have a typical individual income tax but does levy a 7.0 percent tax on capital gains income. Washington does not have a corporate income tax but does levy a state gross receipts tax. Washington has a 6.50 percent state sales tax rate and an average combined state and local sales tax rate of 9.38 percent. Washington has a 0.76 percent effective property tax rate on owner-occupied housing value.
Washington has an estate tax. Washington has a 52.8 cents per gallon gas tax rate and a $3.025 cigarette excise tax rate. The State of Washington collects $6,644 in state and local tax collections per capita. Washington has $11,632 in state and local debt per capita and has a 103 percent funded ratio of public pension plans. Overall, Washington’s tax system ranks 35th on our 2024 State Business Tax Climate Index.
Each state’s tax code is a multifaceted system with many moving parts, and Washington is no exception. The first step towards understanding Washington’s tax code is knowing the basics. How does Washington State collect tax revenue? Click the tabs below to learn more! You can also explore our state tax maps, which are compiled from our annual publication, Facts & Figures 2024: How Does Your State Compare?
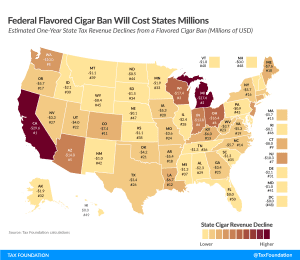
The FDA’s proposal to ban flavored cigars would carry significant revenue implications for many state governments.
7 min read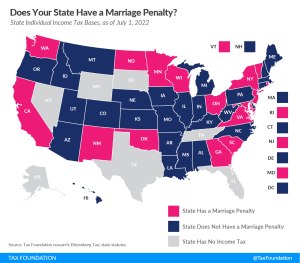
A marriage penalty exists when a state’s income brackets for married taxpayers filing jointly are less than double the bracket widths that apply to single filers. In other words, married couples who file jointly under this scenario have a higher effective tax rate than they would if they filed as two single individuals with the same amount of combined income.
2 min read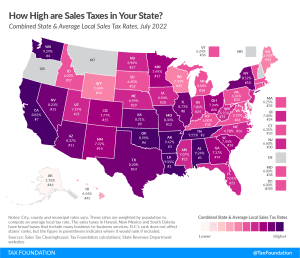
While many factors influence business location and investment decisions, sales taxes are something within policymakers’ control that can have immediate impacts.
12 min read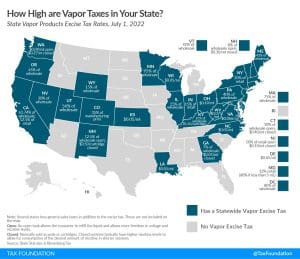
If the policy goal of taxing cigarettes is to encourage cessation, vapor taxation must be considered a part of that policy design.
4 min read
The Kansas experience is so infamous that “what about Kansas?” is almost guaranteed to be a question—sometimes as a retort, but often a genuine expression of concern—any time any state explores tax relief. But what about the other two dozen states that have cut their income taxes since then?
6 min read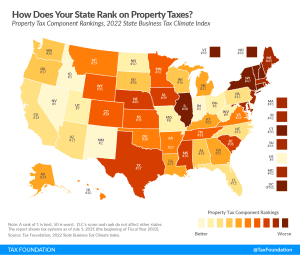
Which states have the highest property taxes in 2022? See how your state compares in property taxes across the United States
3 min read
The sales tax is too important a part of states’ revenue toolkits to be permitted further erosion, making sales tax modernization a vital project of the 2020s.
17 min read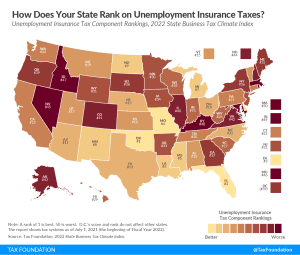
Ranking unemployment insurance tax codes on the 2022 State Business Tax Climate Index. Learn more about state unemployment insurance tax code and systems.
4 min read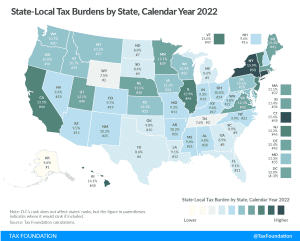
Tax burdens rose across the country as pandemic-era economic changes caused taxable income, activities, and property values to rise faster than net national product. Tax burdens in 2020, 2021, and 2022 are all higher than in any other year since 1978.
24 min read
After a whirlwind of cuts and reforms in 2021, it looks like 2022 might be an even bigger year for state tax codes. Republican and Democratic governors alike used their annual State of the State addresses to call for tax reform, and there is already serious momentum from state lawmakers nationwide to get the job done.
3 min read