Budget Reconciliation: Tracking the 2025 Trump Tax Cuts
Our experts are providing the latest details and analysis of proposed federal tax policy changes.
14 min readThe mission of our federal program is to promote tax and fiscal policy that leads to greater U.S. competitiveness, higher economic growth, and improved quality of life for all taxpayers.
We have several projects, such as the Growth and Opportunity Agenda and Options for Reforming America’s Tax Code, which help us educate taxpayers, journalists, and policymakers on how the U.S. tax system works and the impact of federal tax changes on taxpayers and the economy.
Our Center for Federal Tax Policy hosts Tax Foundation University, a crash course designed to educate congressional staff on the economics of tax policy. Our experts are also a go-to source in the media and are frequently cited in top outlets like The Wall Street Journal, The New York Times, and The Washington Post. See Our Experts
Since 2012, we have used our Taxes and Growth (TAG) macroeconomic model to analyze dozens of legislative and campaign tax proposals, including every major tax plan put forth during the 2016 presidential campaigns, the House GOP’s 2016 Tax Reform Blueprint, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, and President Biden’s tax reform agenda. See Our Economic and Tax Modeling
For a look at where tax modeling started, explore the extensive body of work from the Institute for Research on the Economics of Taxation (IRET), the think tank that pioneered dynamic tax modeling. Explore the IRET Archives
Tax Cuts and Jobs Act Tariffs & Trade Debt & Deficits Trump Tax Plan
Cost Recovery | Taxes & Inflation | Taxes on Savers & Investors | Carbon Taxes

Our experts are providing the latest details and analysis of proposed federal tax policy changes.
14 min read
Permanently extending the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act would boost long-run economic output by 1.1 percent, the capital stock by 0.7 percent, wages by 0.5 percent, and hours worked by 847,000 full-time equivalent jobs.
6 min read
The tariffs amount to an average tax increase of nearly $1,200 per US household in 2025.
37 min read
Unless Congress acts, Americans are in for a tax hike in 2026.
3 min read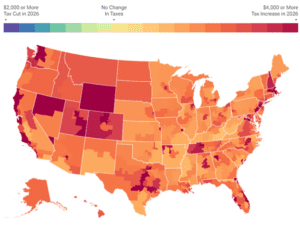
At the end of 2025, the individual tax provisions in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) expire all at once. Without congressional action, most taxpayers will see a notable tax increase relative to current policy in 2026.
4 min read
Policymakers should have two priorities in the upcoming economic policy debates: a larger economy and fiscal responsibility. Principled, pro-growth tax policy can help accomplish both.
21 min read
This tax reform plan would boost long-run GDP by 2.5%, grow wages by 1.4%, and add 1.3M jobs, all while collecting a similar amount of tax revenue as the current code and reducing the long-run debt burden.
38 min read
Given the poor state of the budget process and worsening debt trajectory, lawmakers should move boldly and quickly to address the issue, including via a fiscal commission process. Issues to consider should include reforms to both spending and taxes.
42 min read
A growing international tax agreement known as Pillar Two presents two new threats to the US tax base: potential lost revenue and limitations on Congress’s ability to set its own tax policy.
39 min read
Due to a legislative oversight, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act excluded the category of qualified improvement property investment from 100 percent bonus depreciation.
12 min read
Changes to the way we tax long-term savings could remove the excess tax burden on saving and investment, helping individuals to better provide for their financial future.
15 min read
Taxes matter to investment decisions. Global tax collectors must weigh the marginal benefit of additional revenues against the economic harm high business taxes could cause.
19 min read
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act moved the U.S. toward more of a territorial corporate tax system used by most other OECD countries. However, the U.S. law contains key differences in the treatment of foreign profits.
24 min read
Congress should allow these tax extenders to expire and instead focus on making permanent features of the tax code that move it toward a more ideal system, such as full expensing.
12 min read
In an attempt to provide a realistic, data-driven analysis of federal tax policy, the Tax Foundation has developed a General Equilibrium Model to simulate the effects of tax policies on the economy and on government revenues and budgets.
6 min read