The economic crisis caused by the coronavirus pandemic poses a triple challenge for tax policy in the United States. Lawmakers are tasked with crafting a policy response that will accelerate the economic recovery, reduce the mounting deficit, and protect the most vulnerable.
To assist lawmakers in navigating the challenge, and to help the American public understand the tax changes being proposed, the Tax Foundation’s Center for Federal Tax Policy modeled how 70 potential changes to the tax code would affect the U.S. economy, distribution of the tax burden, and federal revenue.
In tax policy there is an ever-present trade-off among how much revenue a tax will raise, who bears the burden of a tax, and what impact a tax will have on economic growth. Armed with the information in our new book, Options for Reforming America’s Tax Code 2.0, policymakers can debate the relative merits and trade-offs of each option to improve the tax code in a post-pandemic world.
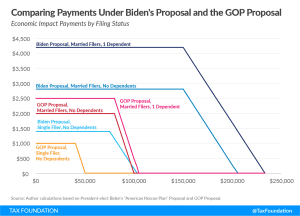
Modeling Different Proposals for Round Three Direct Payments
President Biden is calling for a third round of economic impact payments to households as part of his $1.9 trillion American Rescue Plan. Under the plan, the payments would be $1,400 per person, topping off the recent round of $600 payments for a combined $2,000 per person. Senate Republicans have proposed payment amounts of $1,000 per individual and $500 per dependent, lower income thresholds, and faster phaseout rates.
5 min read
Washington State Lawmakers Considering New Bans and Higher Taxes on Nicotine Products
Washington state lawmakers have proposed a bill that would make it the second state to ban all flavored tobacco and the first to impose a nicotine cap on vapor products, and would increase taxes on vapor to among the highest in the nation.
5 min read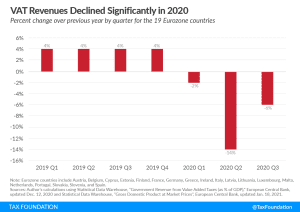
Value-added Taxes in the Pandemic
Many governments have chosen to use VAT as a tool to provide tax relief for consumption in various sectors throughout the pandemic, but in the long term, VAT should not be used as a tool for relief.
3 min read
Wisconsin’s PPP Loan Recipients Face Hundreds of Millions in Surprise Taxes
Unless the legislature acts, businesses that have received PPP loans and related federal assistance will face $457 million in state taxes through 2024—with more than half of those taxes coming due this spring—despite Wisconsin being on track to see continued general fund revenue growth even amid the pandemic.
4 min read
What the GameStop Saga Can Teach Us About Mark-to-Market Taxation of Capital Gains
Whether you see the GameStop saga as a Robin Hood-style victory for the little guys or as a case of disruptive investor hysteria, it provides an interesting case study in just how badly the mark-to-market treatment of capital gains income could go awry.
6 min read
Washington State Floats a Wealth Tax Which Relies Almost Exclusively on Four People
What happens if you create a tax and its base is, for all intents and purposes, four people? If some Washington lawmakers had their way, we might find out.
5 min read
Using Carbon Tax Revenue to Grow the Economy
The economy and climate change are two challenges the Biden administration has identified as priorities. One way to address both issues at the same time is to enact a carbon tax to discourage carbon emissions, and to use the resulting carbon tax revenue to lower—or in the case of the TCJA’s individual provisions, avoid increases of—other, more distortive, types of taxes. This would not only address the challenges of climate change but also support the economy.
3 min read
5 Observations on Janet Yellen’s Recent Confirmation Testimony
In her recent confirmation hearing, economist Janet Yellen, President Biden’s choice for Treasury Secretary, sought to reassure markets that the new administration would not raise corporate taxes until the economy improves. At the same time, however, she sent a troubling signal that when they do push for higher corporate tax rates, they would do so in coordination with other countries so that the U.S. doesn’t lose its competitive edge.
5 min read
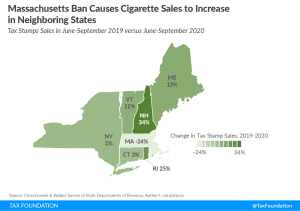
Massachusetts Flavored Tobacco Ban Has Severe Impact on Tax Revenue
The Massachusetts flavored tobacco ban highlights the complications of contradictory tax and regulatory policy, the instability of excise taxes that go beyond pricing in the cost of externalities, and the public risks of driving consumers into the black market through excessive taxation or regulation.
5 min read