The economic crisis caused by the coronavirus pandemic poses a triple challenge for tax policy in the United States. Lawmakers are tasked with crafting a policy response that will accelerate the economic recovery, reduce the mounting deficit, and protect the most vulnerable.
To assist lawmakers in navigating the challenge, and to help the American public understand the tax changes being proposed, the Tax Foundation’s Center for Federal Tax Policy modeled how 70 potential changes to the tax code would affect the U.S. economy, distribution of the tax burden, and federal revenue.
In tax policy there is an ever-present trade-off among how much revenue a tax will raise, who bears the burden of a tax, and what impact a tax will have on economic growth. Armed with the information in our new book, Options for Reforming America’s Tax Code 2.0, policymakers can debate the relative merits and trade-offs of each option to improve the tax code in a post-pandemic world.

Focusing on Wealth Inequality Is Counterproductive
While there is more we can do to encourage lower- and middle-class households to save more and build wealth, a closer, more comprehensive look at the data and trends in other countries suggests that America’s wealth gap is not as alarming as some may think.
5 min read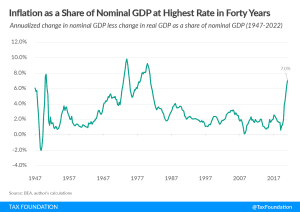
The “Inflation Tax” Is Regressive
A new CBO report reveals that lower- and middle-income households are disproportionately shouldering the burden of this current inflation wave. And historical analysis suggests there is much more to come.
5 min read
Impact of Italian Elections on National Tax Policy and EU Fiscal Policy
In the EU, Italy plays an important role in economic policy. If the EU wants to further develop own resources, it will need the backing of the Italian government—which seems unlikely at the moment.
4 min read
Doing Tax Policy at the Ballot Is Not for the Faint of Heart
Some tax ballot initiatives will be straightforward, some will be complex, and—let’s be honest—some will be a drafting nightmare.
5 min read
The Sticks: Inflation Reduction Act’s Energy-Related Tax Increases
The Inflation Reduction Act primarily uses carrots, not sticks, to incentivize reductions in carbon emissions. It creates or expands tax credits for various low- or no-emission technologies, rather than imposing a generalized penalty for emissions, such as a carbon tax.
5 min read
Influential Tax Reformer Ernest S. Christian, Jr., Leaves Legacy—and Blueprint
Ernest S. Christian, Jr., (1937-2022) was one of the tax policy community’s most distinguished and influential experts, showing us how effective sound tax policy can be. He passed away on September 13th, leaving behind a legacy of tax reform.
4 min read
Breaking Down the Inflation Reduction Act’s Green Energy Tax Credits
The Inflation Reduction Act created numerous tax subsidy programs intended to accelerate the transition to a greener economy.
8 min read
Ensuring Tax Rates Don’t Rise with Inflation
If ever there was a paycheck protection program, defending people from bracket creep may be the most important one ever designed.
6 min read
States That Might Tax Student Loan Debt Cancellation
Will states consider student loan forgiveness a taxable event? In some states, the answer could be yes.
5 min read
Taxes and the UK’s new Prime Minister
In an already-challenging economic environment, new UK Prime Minister Liz Truss must get tax rates correct to avoid over-burdening a population and business sector facing immense uncertainty. Focusing only on rates while ignoring the base misses an opportunity for real, pro-growth reform.
4 min read