We often hear that one of the primary goals of fundamental tax reform is to “broaden the base and lower taxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities. rates.” But as many of the presidential candidates have found in crafting their tax reform plans, the extreme progressivity of the individual tax code makes broadening the base and lowering the rate an exercise in raising taxes on the poor and cutting taxes on the rich—hardly a winning political message.
Over the past 20 years or so, lawmakers have created or expanded numerous tax credits aimed at helping the poor and middle-class, the most generous of which are the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and the child credit (now valued at $1,000 per-child). What makes these credits especially beneficial to lower-income taxpayers is that they are refundable, which means that you can receive the full value of the credit even if you don’t have an income tax liability at all.
For example, if your tax liability is $500, but you are eligible for a $1,000 credit, then the credit will not only erase your tax liability, but the IRS will send you a $500 check for the refundable portion of the credit.
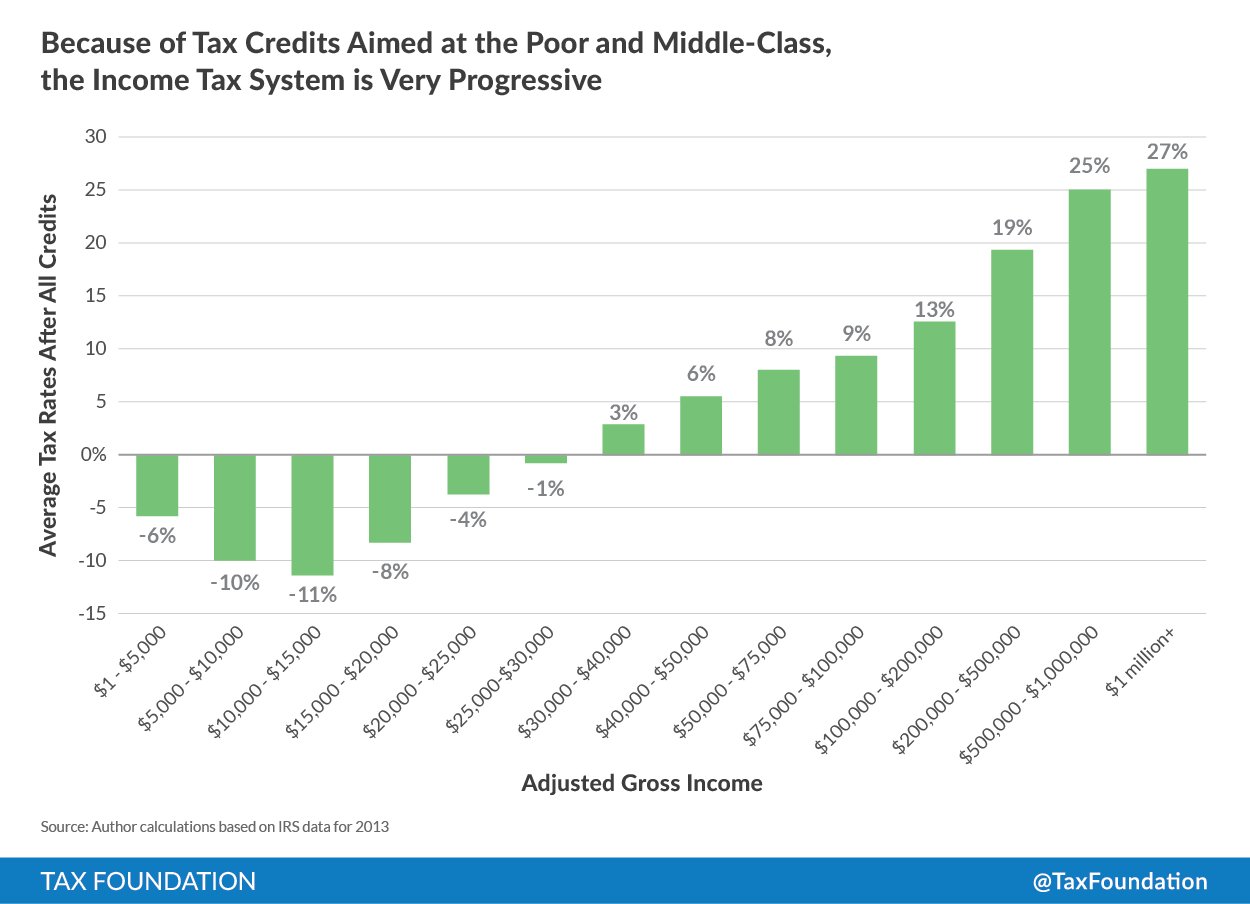
The chart below shows the impact that refundable tax credits have had on making the income tax system so progressive, meaning very beneficial to the poor and with the rich bearing a disproportionate share of the burden. The chart displays the average tax rates that taxpayers in various income groups pay after they’ve benefited from all of the credits and deductions they are eligible for. When we look at the aggregate IRS data for taxpayers earning roughly below $30,000, we see that they have a negative average tax rateThe average tax rate is the total tax paid divided by taxable income. While marginal tax rates show the amount of tax paid on the next dollar earned, average tax rates show the overall share of income paid in taxes. . What that means, is that the vast majority of people in that income group receive substantial refundable tax credits relative to their incomes.
The chart also shows the impact that credits have had on reducing the tax liability of middle-class families as well. Indeed, taxpayers in income groups ranging from $30,000 to $100,000 typically have average tax rates in the single digits, from 3 percent to 9 percent.
While the average tax rates of individual taxpayers may vary, looking at income groups, we typically see double-digit average tax rates starting with taxpayers earning more than $200,000, and we see average tax rates over 20 percent for taxpayers earning more than $500,000. As a group, taxpayers earning more than $1 million have average tax rate of 27 percent.
For supporters of the Flat Tax in particular, which proposes to eliminate all credits and deductions and levy a single rate for all taxpayers, the extreme progressivity of the income tax system poses a particularly challenging problem. However, as we’ve seen, even the non-Flat TaxAn income tax is referred to as a “flat tax” when all taxable income is subject to the same tax rate, regardless of income level or assets. plans have had to navigate this issue.
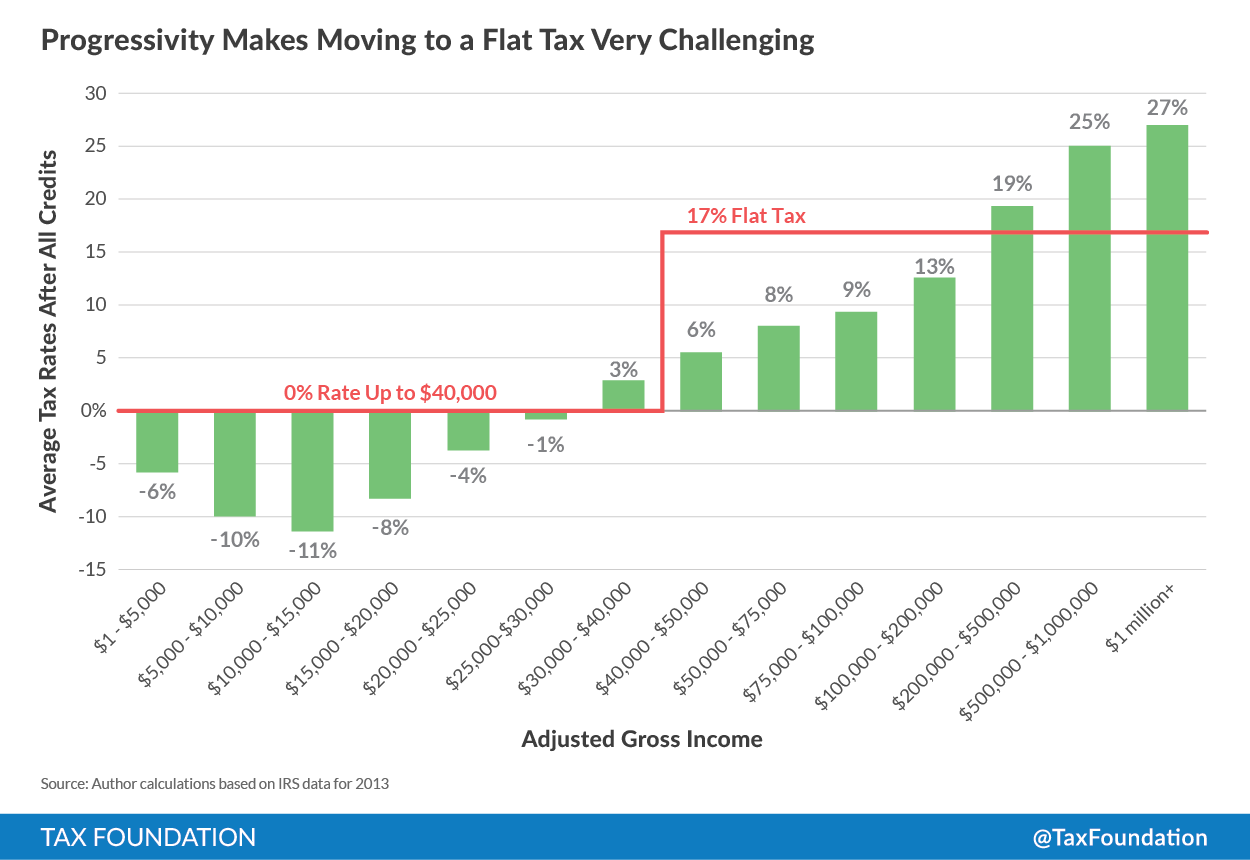
As the next chart illustrates, broadening the tax base by eliminating all credits and deductions will, by definition, “raise taxes on the poor” because doing so repeals the refundable tax credits that supplement their incomes. Although most forms of the Flat Tax try to protect the poor by having a generous personal or family allowance—such as the $10,000 per-person family allowance shown here—even this nod toward progressivity can inadvertently raises taxes on the poor because of the loss of their refundable checks from the IRS.
Meanwhile, a single rate tax system, such as the 17 percent rate shown here, can also end up raising taxes on the middle-class because so many of these taxpayers have low average tax credits due to the child credit and other targeted provisions. Indeed, in this very simplified example, taxpayers in income groups ranging from $50,000 to $200,000 would see an increase in their taxes under a flat rate system.
Much to the shock of would-be tax reformers who would broaden the base and lower tax rates, the only beneficiaries of a single rate tax system are the rich and taxpayers with incomes above $200,000 per year. Although the biggest winners would be taxpayers with incomes of $500,000 and over $1 million.
Needless to say, cutting taxes for the rich and raising taxes on the poor is a public relations nightmare for most politicians. To one degree or another, nearly all of the Republican presidential candidates who have released detailed tax plans so far (Senator Paul, Senator Rubio, and Governor Bush) have had to navigate these distributional waters. By and large, they all chose to keep the refundable tax credits out of deference to distributional concerns as they lowered top tax rates.
Donald Trump, however, actually narrowed the tax baseThe tax base is the total amount of income, property, assets, consumption, transactions, or other economic activity subject to taxation by a tax authority. A narrow tax base is non-neutral and inefficient. A broad tax base reduces tax administration costs and allows more revenue to be raised at lower rates. by created a zero income tax bracket of $25,000 for singles and $50,000 for married couples. By his own admission, his plan would eliminate the income tax burden for 73 million taxpayers—half of the roughly 145 million tax filers.
In addition to knocking millions of Americans off the tax rolls completely, my colleague Alan Cole has shown that Trump’s plan would mean a large tax cut for the middle-class as well. Ironically, Trump was still criticized by numerous pundits for cutting taxes for the rich, but such is the inevitable result of lowering rates in a highly progressive system.
As a result of their two-decade long efforts to help the poor and middle-class through the tax code, lawmakers have painted themselves into a box. The tax code is so progressive now, and so many taxpayers are net beneficiaries of generous refundable tax credits, that it is almost impossible politically to “broaden the base, and lower tax rates.”
This is just one of the largest hurdles lawmakers face in overhauling America’s byzantine tax code, and that’s before they even try to take on the special interests. But as Thomas Jefferson said, “With great risk comes great gain.”
Share this article