Taxes, Fiscal Policy, and Inflation
Consumer prices rose by 7 percent in 2021, the highest annual rate of inflation since 1982. Where did this inflation come from and what might its impacts be? Tax and fiscal policy offer important clues.
5 min read
Consumer prices rose by 7 percent in 2021, the highest annual rate of inflation since 1982. Where did this inflation come from and what might its impacts be? Tax and fiscal policy offer important clues.
5 min read
While hoping for inflation’s continued decline, policymakers should finish the job and index the tax code to prepare for future bouts of high inflation and as a contingency in case it takes longer to defeat elevated inflation than expected.
4 min read
Inflation is often called a hidden tax, but in many states it yields a far more literal tax increase as tax brackets fail to adjust for changes in consumer purchasing power.
5 min read
As members of Congress prepare to address the expiration of the TCJA, they should appreciate how revenues have evolved since 2017.
4 min read
The European Union’s experience with high inflation highlights the critical need for adaptive fiscal policies. Best practices drawn from the academic literature recommend implementing automatic adjustment mechanisms with a certain periodicity and based on price increases.
31 min read
Rather than adopt temporary policies that phase out and expire, policymakers should focus their efforts on long-term reforms to support investment.
6 min read
Lawmakers should see 2025 as an opportunity to consider more fundamental tax reforms. While the TCJA addressed some of the deficiencies of the tax code, it by no means addressed them all.
8 min read
To recover from the pandemic and put the global economy on a trajectory for growth, policymakers need to aim for more generous and permanent capital allowances. This will spur real investment and can also contribute to more environmentally friendly production across the globe.
31 min read
Improving the country’s fiscal situation won’t be comfortable, but economic growth can help cushion the blow.
3 min read
Two bills in Georgia will lower the flat individual income tax rate and align the corporate income tax rate with the individual income tax rate.
4 min read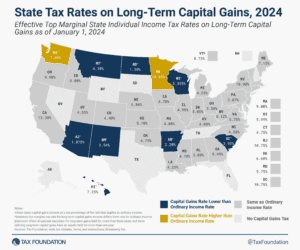
Savings and investment are critical activities, both for individuals’ and families’ financial security and for the health of the national economy as a whole. As such, policymakers should consider how they can help mitigate—rather than add to—tax codes’ biases against saving and investment.
5 min read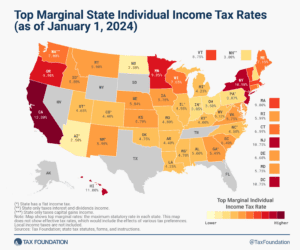
Individual income taxes are a major source of state government revenue, accounting for more than a third of state tax collections. How do income taxes compare in your state?
8 min read
The U.S. House of Representatives has passed a highly anticipated bipartisan tax deal. The Tax Relief for American Workers and Families Act now awaits action in the Senate.
6 min read
Nebraskans need property tax relief and there are sound ways to provide it. However, increasing the sales tax rate to the highest in the country and dramatically increasing cigarette excises is not sound tax policy.
5 min read
Thirty-four states will ring in the new year with notable tax changes, including 15 states cutting individual or corporate income taxes (and some cutting both).
17 min read
What historical lessons of wartime finance can Ukrainian and EU policymakers learn to put Ukraine’s economy on a path to success during, and especially after, the war?
5 min read
Explore the IRS inflation-adjusted 2024 tax brackets, for which taxpayers will file tax returns in early 2025.
4 min read
Policymakers on Capitol Hill should prioritize permanent pro-growth policy in the coming years as the economy struggles with inflation and the recovery from the pandemic.
4 min read
At the most recent Republican primary debate, former governor and United Nations ambassador Nikki Haley (R-SC) proposed eliminating the federal gas tax to lower fuel prices for consumers.
3 min read
In recent years, European countries have undertaken a series of tax reforms designed to maintain tax revenue levels while protecting households and businesses from high inflation.
8 min read
Now is the time for lawmakers to focus on long-term fiscal sustainability, as further delay will only make an eventual fiscal reckoning that much harder and more painful. Congressional leaders should follow through on convening a fiscal commission to deal with the long-term budgetary challenges facing the country.
35 min read
One year after its enactment, there are concerns about the Inflation Reduction Acts overall fiscal impact, the additional complexity it introduces to the tax system, and the sustainability of its initiatives.

GDP stands for gross domestic product and is calculated by measuring a country’s total consumption, government spending, investments, and net exports.
2 min read