The economic crisis caused by the coronavirus pandemic poses a triple challenge for tax policy in the United States. Lawmakers are tasked with crafting a policy response that will accelerate the economic recovery, reduce the mounting deficit, and protect the most vulnerable.
To assist lawmakers in navigating the challenge, and to help the American public understand the tax changes being proposed, the Tax Foundation’s Center for Federal Tax Policy modeled how 70 potential changes to the tax code would affect the U.S. economy, distribution of the tax burden, and federal revenue.
In tax policy there is an ever-present trade-off among how much revenue a tax will raise, who bears the burden of a tax, and what impact a tax will have on economic growth. Armed with the information in our new book, Options for Reforming America’s Tax Code 2.0, policymakers can debate the relative merits and trade-offs of each option to improve the tax code in a post-pandemic world.




How Controlled Foreign Corporation Rules Look Around the World: Germany
Germany has had a Controlled Foreign Corporation (CFC) regime since 1972, when the German Foreign Transactions Tax Act was enacted. Under the German regime, a CFC is a foreign company where its capital or voting rights are either directly or indirectly majority-owned by German residents at the end of its fiscal year.
6 min read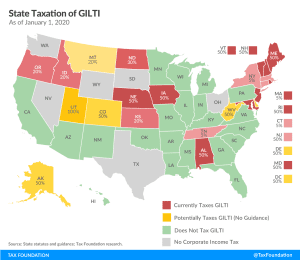
Kansas, Nebraska, and Utah Lawmakers Pursue “Not GILTI” Verdicts
Taxing GILTI puts states at a competitive disadvantage compared to their peers—all for a tax that makes very little sense at the state level, and which legislators never sought in the first place.
5 min read
Toomey Introduces Legislation to Make Bonus Depreciation Permanent and Fix the Retail Glitch
Making 100 percent bonus depreciation permanent avoids the uncertainty associated with the phaseout of a powerful pro-growth policy and would provide a cost-effective boost to long-run economic output, wages, and employment in the United States.
2 min read

Banning Flavored Tobacco Could Have Unintended Consequences
The prospect of a ban on flavored tobacco and nicotine products highlights the complications of contradictory tax and regulatory policy, the instability of excise taxes that go beyond pricing in the cost of externalities, and the public risks of driving consumers into the black market through excessive taxation or regulation.
6 min read
The White House Budget Highlights the Need to Extend Pro-Growth TCJA Business Tax Provisions
Full expensing, if made permanent, would be one of the most cost-effective ways to increase growth as it would produce about 4.5 times more GDP growth per dollar of revenue than making the law’s individual tax provisions permanent, according to our analysis.
3 min read
Bracing for Impact
Though they are limited by both data and assumptions, the OECD will face similar limitations. As policymakers work to fine-tune the proposals under both Pillar 1 and 2 the impact assessment should be a critical part of that discussion.
6 min read