Top Personal Income Tax Rates in Europe, 2024
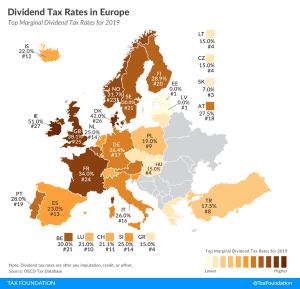
Denmark (55.9 percent), France (55.4 percent), and Austria (55 percent) have the highest top statutory personal income tax rates among European OECD countries.
3 min readProviding journalists, taxpayers, and policymakers with the latest data on taxes and spending is a cornerstone of the Tax Foundation’s educational mission.
As a nonpartisan, educational organization, the Tax Foundation has earned a reputation for independence and credibility.
Our EU tax policy team regularly provides accessible, data-driven insights from sources such as the European Commission, the Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD), and others.
Denmark (55.9 percent), France (55.4 percent), and Austria (55 percent) have the highest top statutory personal income tax rates among European OECD countries.
3 min read
A few European countries have made changes to their VAT rates, including the Czech Republic, Estonia, Switzerland, and Turkey.
3 min read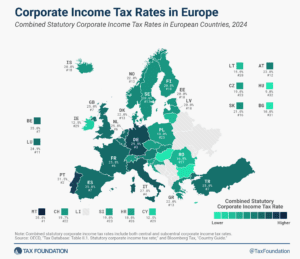
Like most regions around the world, European countries have experienced a decline in corporate income tax rates over the past four decades, but the average corporate income tax rate has leveled off in recent years.
2 min read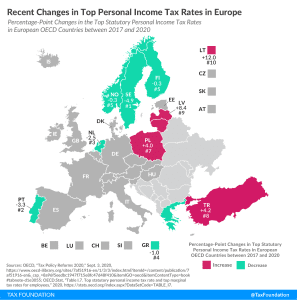
Ten European OECD countries recently changed their top personal income tax rates. Of the ten countries, six cut their top personal income tax rates while the other four raised their top rates.
4 min read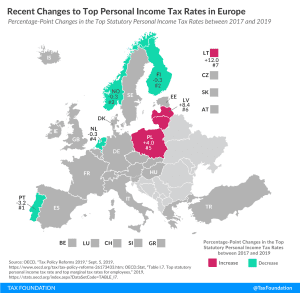
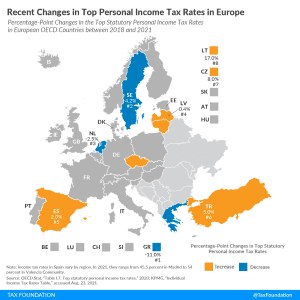
In the past three years, eight European OECD countries changed their top personal income tax rate, of which four of them cut their top personal income tax rates.
3 min read
Denmark (55.9 percent), France (55.4 percent), and Austria (55 percent) have the highest top statutory personal income tax rates among European OECD countries.
3 min read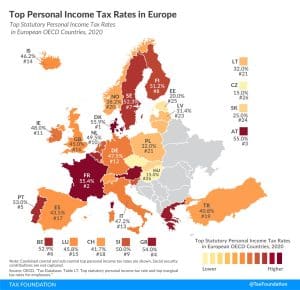
Most countries’ personal income taxes have a progressive structure, meaning that the tax rate paid by individuals increases as they earn higher wages. The highest tax rate individuals pay differs significantly across Europe, with Denmark (55.9 percent), France (55.4 percent), and Austria (55 percent) having the highest top statutory personal income tax rates among European OECD countries.
3 min read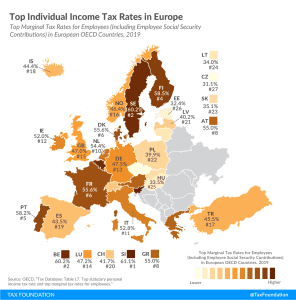
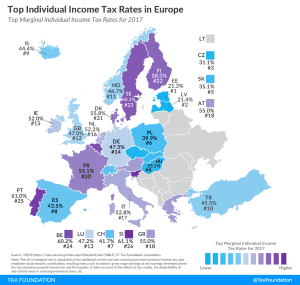
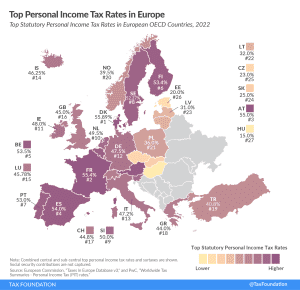
Denmark (55.9 percent), France (55.4 percent), and Austria (55 percent) have the highest top statutory personal income tax rates among European OECD countries.
2 min read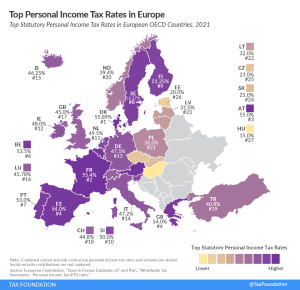
Denmark (55.9 percent), France (55.4 percent), and Austria (55 percent) have the highest top statutory personal income tax rates among European OECD countries.
2 min read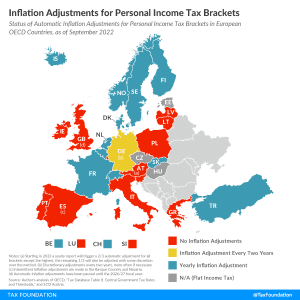
With continued concerns over inflation, individuals may be wondering how their tax bills will be impacted. Less than half of OECD countries in Europe automatically adjust income tax brackets for inflation every year.
2 min read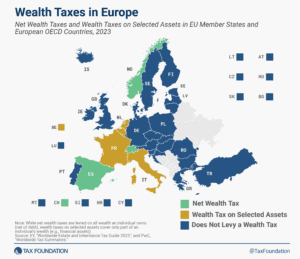
Only three European countries levy a net wealth tax—Norway, Spain, and Switzerland. France and Italy levy wealth taxes on selected assets.
4 min read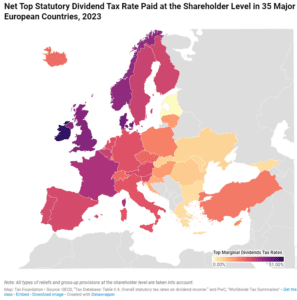
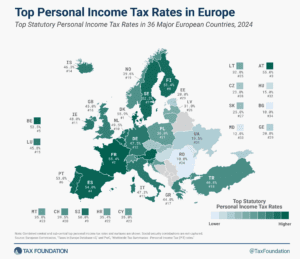
In many countries, corporate profits are subject to two layers of taxation: the corporate income tax at the entity level when the corporation earns income, and the dividend tax or capital gains tax at the individual level when that income is passed to its shareholders as either dividends or capital gains.
2 min read
Varying local trade tax rates impact business investment and local government revenue across Germany’s municipalities.
4 min read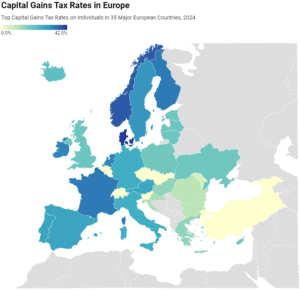
In many European countries, investment income, such as dividends and capital gains, is taxed at a different rate than wage income.
2 min read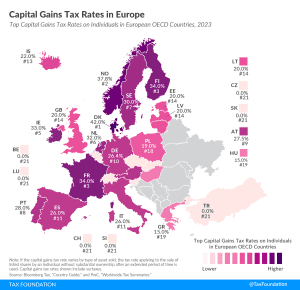
In many countries, investment income, such as dividends and capital gains, is taxed at a different rate than wage income. Denmark levies the highest top capital gains tax of all countries covered, at a rate of 42 percent. Norway levies the second-highest top capital gains tax at 37.8 percent. Finland and France follow, at 34 percent each.
4 min read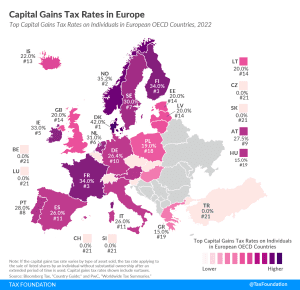
In many countries, investment income, such as dividends and capital gains, is taxed at a different rate than wage income. Denmark levies the highest top capital gains tax among European OECD countries, followed by Norway, Finland, and France.
4 min read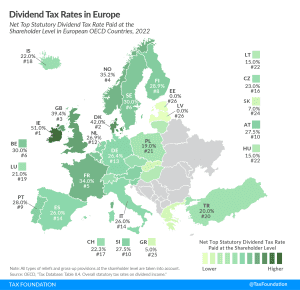
In many countries, corporate profits are subject to two layers of taxation: the corporate income tax at the entity level when the corporation earns income, and the dividend tax or capital gains tax at the individual level when that income is passed to its shareholders as either dividends or capital gains.
3 min read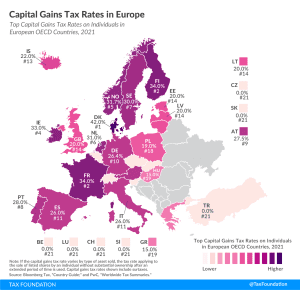
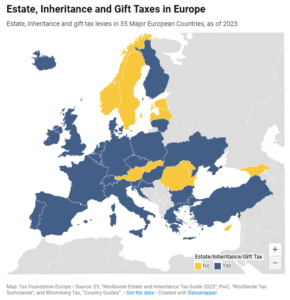
As tempting as inheritance, estate, and gift taxes might look—especially when the OECD notes them as a way to reduce wealth inequality—their limited capacity to collect revenue and their negative impact on entrepreneurial activity, saving, and work should make policymakers consider their repeal instead of boosting them.
2 min read