Top Personal Income Tax Rates in Europe, 2025
Denmark (55.9 percent), France (55.4 percent), and Austria (55 percent) levy the highest top personal income tax rates in Europe.
4 min readProviding journalists, taxpayers, and policymakers with the latest data on taxes and spending is a cornerstone of the Tax Foundation’s educational mission.
As a nonpartisan, educational organization, the Tax Foundation has earned a reputation for independence and credibility. Our global tax policy team regularly provides accessible, data-driven insights, including a survey of corporate tax rates around the world, from sources such as the Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD), the European Commission, and others.
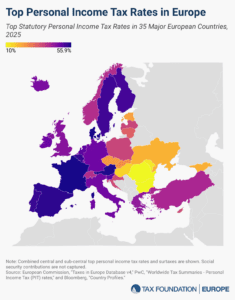
Denmark (55.9 percent), France (55.4 percent), and Austria (55 percent) levy the highest top personal income tax rates in Europe.
4 min read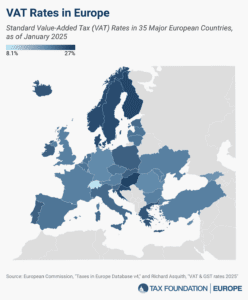
More than 175 countries worldwide—including all major European countries—levy a value-added tax (VAT) on goods and services. EU Member States’ VAT rates vary across countries, though they’re somewhat harmonized by the EU.
5 min read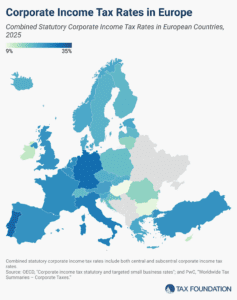
Some European countries have raised their statutory corporate rates over the past year, including Czechia, Estonia, Iceland, Lithuania, and Slovenia.
3 min read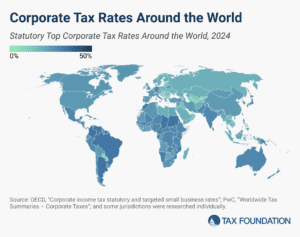
The worldwide average statutory corporate tax rate has consistently decreased since 1980 but has leveled off in recent years. In the US, the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act brought the country’s statutory corporate income tax rate from the fourth highest in the world closer to the middle of the distribution.
18 min read
Developed countries raise tax revenue through individual income taxes, corporate income taxes, social insurance taxes, taxes on goods and services, and property taxes—the combination of which determines how distortionary or neutral a tax system is.
4 min read
To recover from the pandemic and put the global economy on a trajectory for growth, policymakers need to aim for more generous and permanent capital allowances. This will spur real investment and can also contribute to more environmentally friendly production across the globe.
33 min read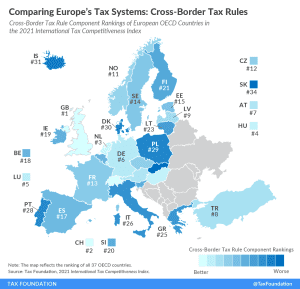
Cross-border tax rules define how income earned abroad and by foreign entities are taxed domestically, making them an important element of each country’s tax code.
3 min read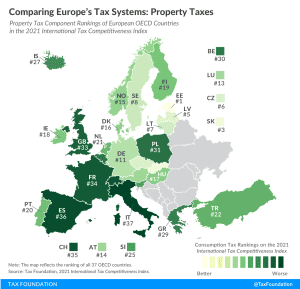
According to the 2021 International Tax Competitiveness Index, Switzerland has the best-structured consumption tax among OECD countries while Poland has the worst-structured consumption tax code.
2 min read
A new report shows that corporate tax rates around the world continue to level off. “We aren’t seeing a race to the bottom, we’re seeing a race toward the middle,” said Sean Bray, global policy analyst at the Tax Foundation.
24 min read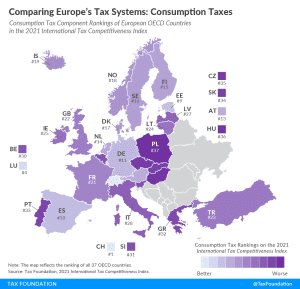
According to the 2021 International Tax Competitiveness Index, Switzerland has the best-structured consumption tax among OECD countries while Poland has the worst-structured consumption tax code.
2 min read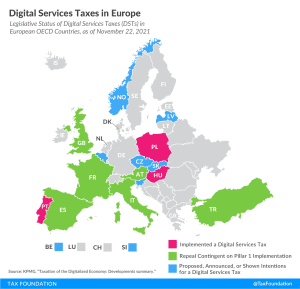
Despite ongoing multilateral negotiations in the OECD, about half of all European OECD countries have either announced, proposed, or implemented their own unilateral digital services tax.
7 min read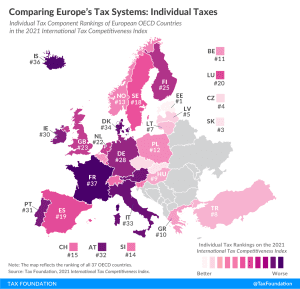
France’s individual income tax system is the least competitive of all OECD countries. It takes French businesses on average 80 hours annually to comply with the income tax.
3 min read