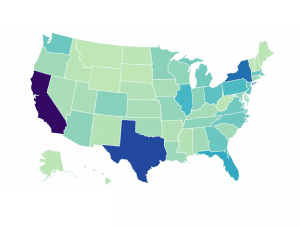
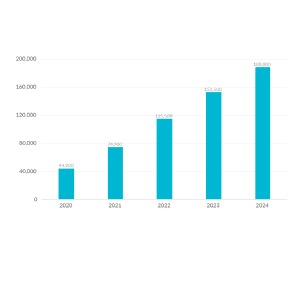
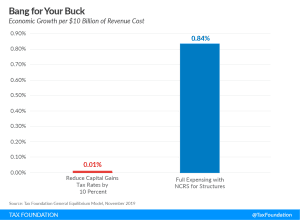
Estimated Impact of Improved Cost Recovery Treatment by State
We estimate that moving to permanent full expensing and neutral cost recovery for structures would add more than 1 million full-time equivalent jobs to the long-run economy and boost the long-run capital stock by $4.8 trillion.
4 min read