International Tax Competitiveness Index
The Tax Foundation' s International Tax Competitiveness Index (ITCI) measures the degree to which the 38 OECD countries' tax systems promote competitiveness through low tax burdens on business investment and neutrality through a well-structured tax code. The ITCI considers more than 40 variables across five categories: Corporate Taxes, Individual Taxes, Consumption Taxes, Property Taxes, and International Tax Rules.
The ITCI attempts to display not only which countries provide the best tax environment for investment but also the best tax environment for workers and businesses.
Sources of Revenue in Latvia
Countries raise tax revenue through a mix of individual income taxes, corporate income taxes, social insurance taxes, taxes on goods and services, and property taxes. The mix of tax policies can influence how distortionary or neutral a tax system is. Taxes on income can create more economic harm than taxes on consumption and property. However, the extent to which an individual country relies on any of these taxes can differ substantially.
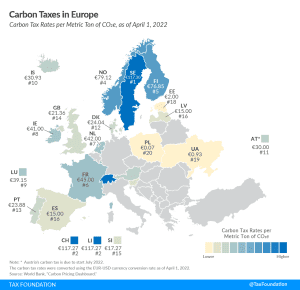
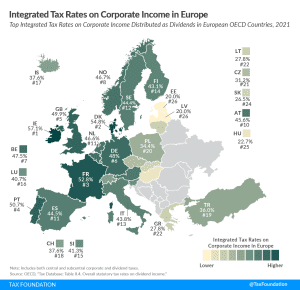
Corporate Taxation in Latvia
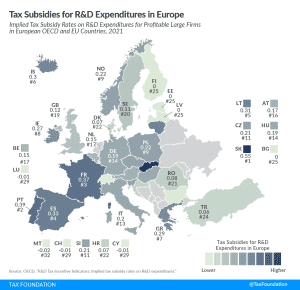
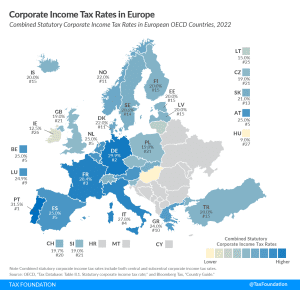
The corporate income tax is a tax on the profits of corporations. All OECD countries levy a tax on corporate profits, but the rates and bases vary widely from country to country. Corporate income taxes are the most harmful tax for economic growth, but countries can mitigate those harms with lower corporate tax rates and generous capital allowances.
Capital allowances directly impact business incentives for new investments. In most countries, businesses are generally not allowed to immediately deduct the cost of capital investments. Instead, they are required to deduct these costs over several years, increasing the tax burden on new investments. This can be measured by calculating the percent of the present value cost that a business can deduct over the life of an asset. Countries with more generous capital allowances have tax systems that are more supportive to business investment, which underpins economic growth.
Individual Taxation in Latvia
Individual taxes are one of the most prevalent means of raising revenue to fund government across the OECD. Individual income taxes are levied on an individual's or household's income to fund general government operations. These taxes are typically progressive, meaning that the rate at which an individual's income is taxed increases as the individual earns more income.
In addition, countries have payroll taxes. These typically flat-rate taxes are levied on wage income in addition to a country's general individual income tax. However, revenue from these taxes is typically allocated specifically toward social insurance programs such as unemployment insurance, government pension programs, and health insurance.
High marginal income tax rates impact decisions to work and reduce the efficiency with which governments can raise revenue from their individual tax systems.
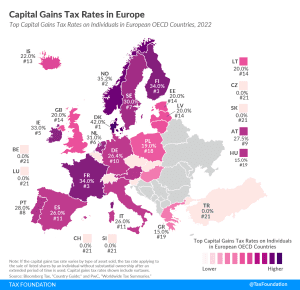
Capital gains and dividend income—if not included in the individual income tax—are typically taxed at a flat rate.
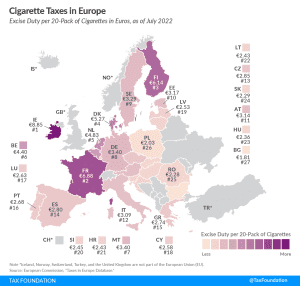
Consumption Taxes in Latvia
Consumption taxes are charged on goods and services and can take various forms. In the OECD and most of the world, the value-added tax (VAT) is the most common consumption tax. Most consumption taxes either do not tax intermediate business inputs or provide a credit for taxes already paid on inputs, which avoids the problem of tax pyramiding, whereby the same final good or service is taxed multiple times in the production process. The exclusion of business inputs makes a consumption tax one of the most economically efficient means of raising tax revenue.
However, many countries fail to define their tax base correctly. To minimize distortions, all final consumption should be taxed at the same standard rate. However, countries often exempt too many goods and services from taxation or tax them at reduced rates, which requires them to levy higher standard rates to raise sufficient revenue. Some countries also fail to properly exempt business inputs. For example, states in the United States often levy sales taxes on machinery and equipment.
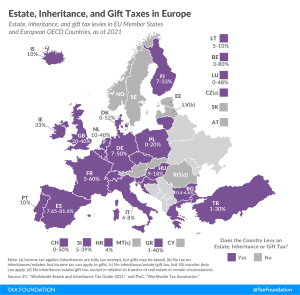
Property Taxes in Latvia
Property taxes apply to assets of an individual or a business. Estate and inheritance taxes, for example, are due upon the death of an individual and the passing of his or her estate to an heir, respectively. Taxes on real property, on the other hand, are paid at set intervals—often annually—on the value of taxable property such as land and houses.
Many property taxes are highly distortive and add significant complexity to the life of a taxpayer or business. Estate and inheritance taxes create disincentives against additional work and saving, which damages productivity and output. Financial transaction taxes increase the cost of capital, which limits the flow of investment capital to its most efficient allocations. Taxes on wealth limit the capital available in the economy, which damages long-term economic growth and innovation.
Sound tax policy minimizes economic distortions. With the exception of taxes on land, most property taxes increase economic distortions and have long-term negative effects on an economy and its productivity.
International Taxes in Latvia
In an increasingly globalized economy, businesses often expand beyond the borders of their home countries to reach customers around the world. As a result, countries need to define rules determining how, or if, corporate income earned in foreign countries is taxed. International tax rules deal with the systems and regulations that countries apply to those business activities.
Tax treaties align many tax laws between two countries and attempt to reduce double taxation, particularly by reducing or eliminating withholding taxes between the countries. Countries with a greater number of partners in their tax treaty network have more attractive tax regimes for foreign investment and are more competitive than countries with fewer treaties.