All Related Articles


Business in America
Who are the workers, consumers, and shareholders who interact with businesses in the U.S.? What forms do these businesses take? How do business taxes impact people’s lives? It is essential we answer these questions in order to design a business tax system that is simple, efficient, and enables economic progress.
5 min read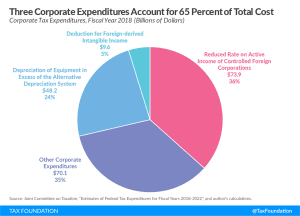
Not All Tax Expenditures Are Equal
The debate in Washington, D.C. often centers around tax expenditures, so-called corporate loopholes, in the tax code. But not all tax expenditures are created equal. Some represent neutral tax treatment and should be left alone, while others are distortionary and should be repealed. Understanding what a tax expenditure represents is essential for understanding how our tax code works for both businesses and individuals.
4 min read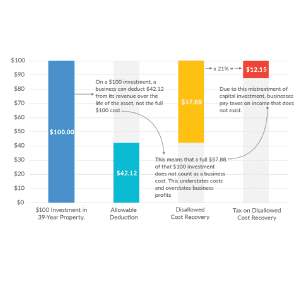
Depreciation Requires Businesses to Pay Tax on Income That Doesn’t Exist
While tax rates matter to businesses, so too does the measure of income to which those tax rates apply. The corporate income tax is a tax on profits, normally defined as revenue minus costs. However, under the current tax code, businesses are unable to deduct the full cost of certain expenses—their capital investments—meaning the tax code is not neutral and actually increases the cost of investment.
3 min read
Taxes on Capital Income Are More Than Just the Corporate Income Tax
The United States’ statutory corporate income tax rate is now more aligned with the rates of other nations . However, taxes on capital income, or corporate investment, are more than just the corporate income tax. Shareholder-level taxes, such as those on dividends and capital gains, also affect incentives to save and invest.
3 min read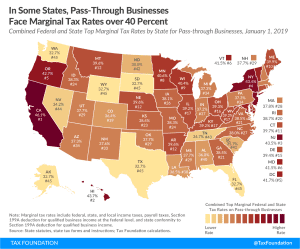
Marginal Tax Rates for Pass-through Businesses Vary by State
Pass-through businesses are now the dominant business form in the U.S., making up more than half of the private sector workforce in every state. Federal taxes on income set a minimum tax rate for pass throughs, but marginal rates for pass throughs vary based on how states tax individual income.
3 min read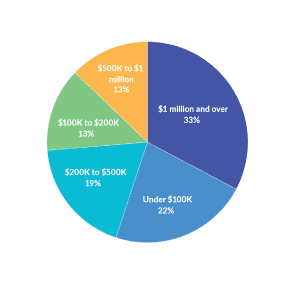
Pass-Through Businesses Q&A
Pass-through businesses are the dominant business structure in America. Pass throughs file more tax returns and report more business income than C corporations. Pass-through businesses are not subject to the corporate income tax, but instead report their income on the individual income tax returns of owners. This blog will address some frequently asked questions about pass-through structure and taxation.
4 min read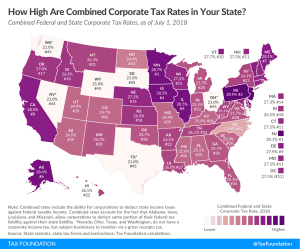
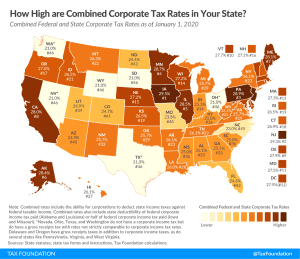
State Corporate Income Taxes Increase Tax Burden on Corporate Profits
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) reduced the U.S. federal corporate income tax rate from 35 percent to 21 percent. However, most U.S. states also tax corporate income. These state-level taxes mean the average statutory corporate income tax rate in the U.S., which combines the average of state corporate income tax rates with the federal corporate income tax rate, is 25.8 percent in 2019.
2 min read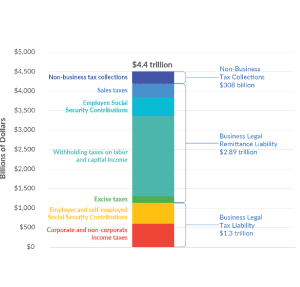
U.S. Businesses Pay or Remit 93 Percent of All Taxes Collected in America
Setting aside the debate over whether a low tax bill is fair, what is missed in such stories is that American businesses are critical to the tax collection system at every level of government—federal, state, and local. Businesses either pay or remit more than 93 percent of all the taxes collected by governments in the U.S. Without businesses as their taxpayers and tax collectors, American governments would not have the resources to provide even the most basic services.
5 min read
Taxable Income vs. Book Income: Why Some Corporations Pay No Income Tax
Why do some companies appear to be profitable but pay little or no federal income taxes? It’s largely due to differences between book and taxable income.
4 min read
The Lowered Corporate Income Tax Rate Makes the U.S. More Competitive Abroad
One of the most significant provisions in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act was the reduction of the U.S. corporate income tax rate from 35 percent to 21 percent. Over time, the lower corporate rate will encourage new investment and lead to additional economic growth. It will make the U.S. more attractive for companies by increasing after-tax returns on investments and will discourage companies from shifting profits to low-tax jurisdictions.
2 min read
2017 GDP and Employment by Industry
In the U.S. economy, there are tens of millions of businesses, including more than 30 million pass-through businesses and more than a million C corporations. Most output and employment come from firms that provide services to consumers—such as education, health care, and social assistance services—though a large share of output and employment still comes from firms in production industries, particularly manufacturing.
2 min read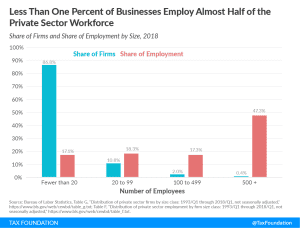
Firm Variation by Employment and Taxes
Less than one percent of businesses employ almost half of the private sector workforce. Large companies pay 89% of corporate income taxes in the United States.
2 min read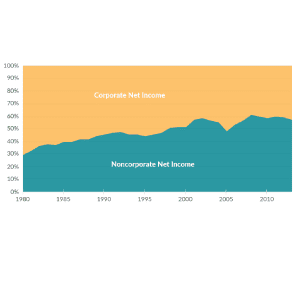
Corporate and Pass-through Business Income and Returns Since 1980
More business income is reported on individual tax returns than corporate returns. The U.S. now has fewer corporations and more individually owned businesses. Corporations make up less than 5 percent of businesses but earn 60 percent of revenues.
3 min read
Tax Policy and Entrepreneurship: A Framework for Analysis
A key element of America’s dynamism problem is a drop in entrepreneurship. Removing tax barriers for entrepreneurs would improve America’s dynamism while making America’s tax code more neutral, efficient, and simple for all taxpayers.
25 min read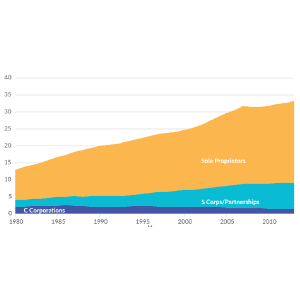
Increasing Individual Income Tax Rates Would Impact a Majority of US Businesses
Since most U.S. businesses are pass-through businesses, such as partnerships, S corporations, LLCs, and sole proprietorships, changes to the individual income tax, especially to top marginal rates, can affect a business’s incentives to invest, hire, and produce.
4 min read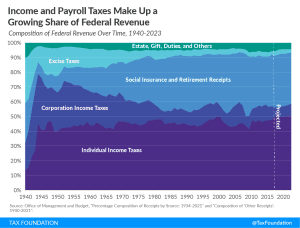
The Composition of Federal Revenue Has Changed Over Time
The federal income tax and federal payroll tax make up a growing share of federal revenue. Individual income taxes have become a central pillar of the federal revenue system, now comprising nearly half of all revenue.
2 min read
Unequal Tax Treatment Is Contributing to Rising Debt Levels for Entrepreneurs
A recent paper discusses two main trends related to U.S. entrepreneurs: the decrease in the number of entrepreneurs and the increase in their borrowing. Entrepreneurs have increased their debt holdings relative to their assets over the past three decades.
3 min read
Reforming the Pass-Through Deduction
Here’s how the new pass-through deduction works and how it can be reformed to be less complex, less prone to abuse, more neutral, and more economically efficient.
49 min read