VAT Rates in Europe, 2021
4 min readBy:More than 140 countries worldwide—including all European countries—levy a Value-Added Tax (VAT) on goods and services. As today’s tax map shows, although harmonized to some extent by the European Union (EU), EU member states’ VAT rates vary across countries.
The VAT is a consumption taxA consumption tax is typically levied on the purchase of goods or services and is paid directly or indirectly by the consumer in the form of retail sales taxes, excise taxes, tariffs, value-added taxes (VAT), or income taxes where all savings are tax-deductible. assessed on the value added in each production stage of a good or service. Every business along the value chain receives a tax credit for the VAT already paid. The end consumer does not, making it a taxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities. on final consumption.
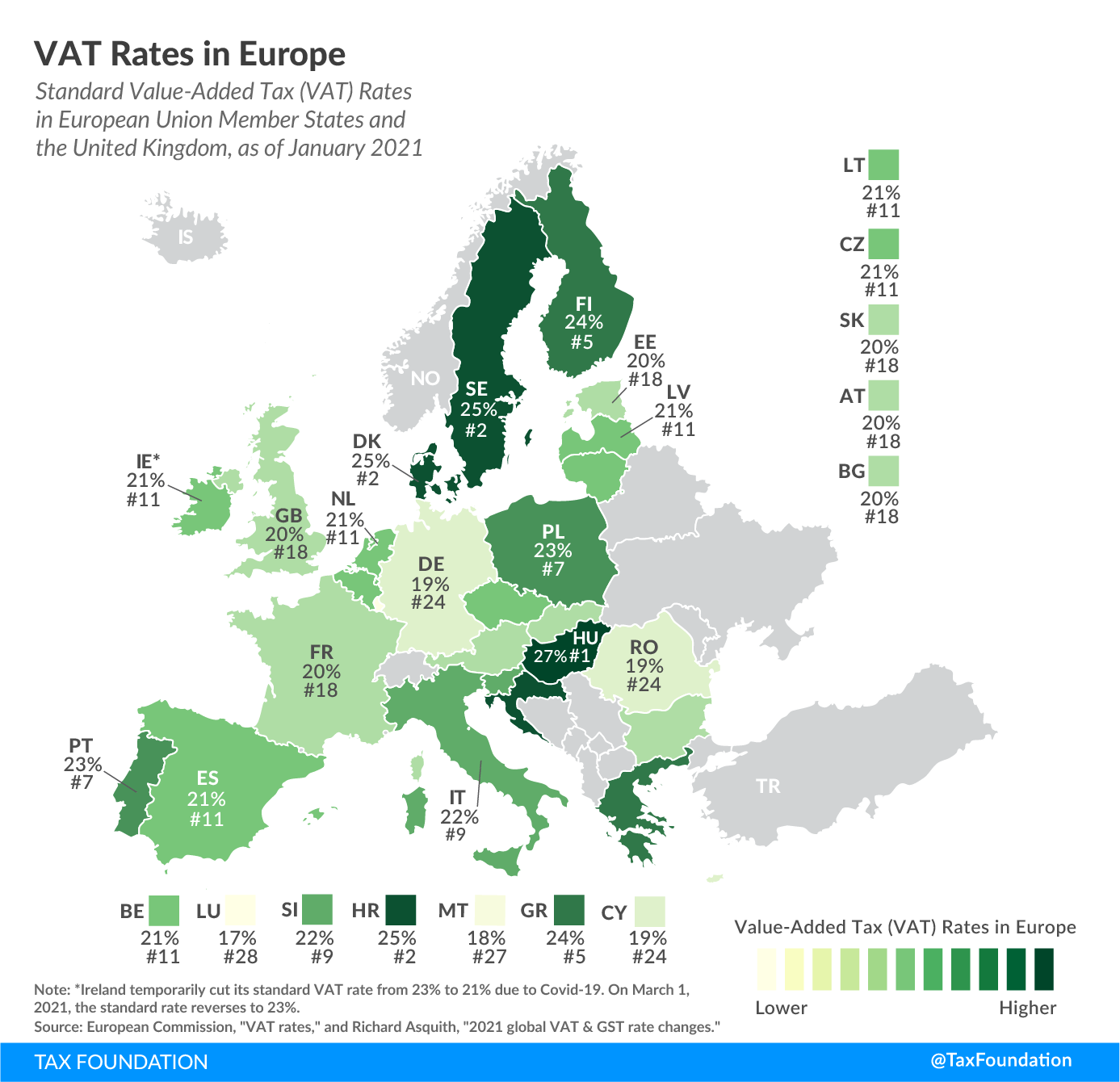
The EU countries with the highest standard VAT rates are Hungary (27 percent), and Croatia, Denmark, and Sweden (all at 25 percent). Luxembourg levies the lowest standard VAT rate at 17 percent, followed by Malta (18 percent), and Cyprus, Germany, and Romania (all at 19 percent). The EU’s average standard VAT rate is 21 percent, six percentage-points higher than the minimum standard VAT rate required by EU regulation.
Several countries implemented temporary VAT rate changes due to COVID-19. VAT rate cuts on goods and services sold by industries particularly affected by the economic fallout of the pandemic—such as the hospitality sector—were most common. Two EU countries took a broader approach: Germany reduced its standard VAT rate from 19 percent to 16 percent and its reduced VAT rate from 7 percent to 5 percent from July 1 to December 31, 2020. Ireland reduced its standard VAT rate from 23 percent to 21 percent from September 1, 2020 to February 28, 2021.
Generally, consumption taxes are an economically efficient way of raising tax revenue. To minimize economic distortions, there is ideally only one standard rate that is levied on all final consumption, with as few exemptions as possible. However, EU countries levy reduced rates and exempt certain goods and services from VAT.
One of the main reasons for reduced VAT rates and VAT-exempted goods/services is the promotion of equity, as lower-income households tend to spend a larger share of income on goods and services such as food and public transport. Other reasons include encouraging the consumption of “merit goods” (e.g., books), promoting local services (e.g., tourism), and correcting externalities (e.g., clean power).
However, evidence shows that reduced VAT rates and VAT exemptions are not necessarily effective in achieving these policy goals and can even be regressive in some instances. Such reduced rates and exemptions can lead to higher administrative and compliance costs and can create economic distortions. To address equity concerns, the OECD instead recommends measures that directly aim at increasing poorer households’ real incomes.
| Country | Super-reduced VAT Rate (%) | Reduced VAT Rate (%) | Parking VAT Rate (%) | Standard VAT Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austria (AT) | – | 10 / 13 | 13 | 20 |
| Belgium (BE) | – | 6 / 12 | 12 | 21 |
| Bulgaria (BG) | – | 9 | – | 20 |
| Croatia (HR) | – | 5 / 13 | – | 25 |
| Cyprus (CY) | – | 5 / 9 | – | 19 |
| Czech Republic (CZ) | – | 10 / 15 | – | 21 |
| Denmark (DK) | – | – | – | 25 |
| Estonia (EE) | – | 9 | – | 20 |
| Finland (FI) | – | 10 / 14 | – | 24 |
| France (FR) | 2.1 | 5.5 / 10 | – | 20 |
| Germany (DE) | – | 7 | – | 19 |
| Greece (GR) | – | 6 / 13 | – | 24 |
| Hungary (HU) | – | 5 / 18 | – | 27 |
| Ireland (IE)* | 4.8 | 9 / 13.5 | 13.5 | 21 |
| Italy (IT) | 4 | 5 / 10 | – | 22 |
| Latvia (LV) | – | 5 / 12 | – | 21 |
| Lithuania (LT) | – | 5 / 9 | – | 21 |
| Luxembourg (LU) | 3 | 8 | 14 | 17 |
| Malta (MT) | – | 5 / 7 | – | 18 |
| Netherlands (NL) | – | 9 | – | 21 |
| Poland (PL) | – | 5 / 8 | – | 23 |
| Portugal (PT) | – | 6 / 13 | 13 | 23 |
| Romania (RO) | – | 5 / 9 | – | 19 |
| Slovakia (SK) | – | 10 | – | 20 |
| Slovenia (SI) | – | 5 / 9.5 | – | 22 |
| Spain (ES) | 4 | 10 | – | 21 |
| Sweden (SE) | – | 6 / 12 | – | 25 |
| United Kingdom (GB) | – | 5 | – | 20 |
|
Notes: *Ireland temporarily cut its standard VAT rate from 23% to 21% due to COVID-19. On or after March 1, 2021, the standard rate reverts to 23%. When one of the major EU VAT directives was adopted in 1991, some EU countries were applying reduced, super-reduced, or zero rates to goods and services that were not specified by the new regulations as falling within the zero-rate or reduced-rate categories. To ease the transition to a standard rate on these goods and services, a so-called “parking rate” was permitted. Although it was intended to be phased out, some countries still apply it. Source: European Commission, “VAT rates,” https://ec.europa.eu/taxation_customs/business/vat/eu-vat-rules-topic/vat-rates_en; and Richard Asquith, “2021 global VAT & GST rate changes,” Avalara, Jan. 1, 2021, https://www.avalara.com/vatlive/en/vat-news/2021-global-vat-rate-changes.html. |
||||
Stay informed on the tax policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted experts delivered straight to your inbox.
Subscribe