Reliance on Consumption Taxes in Europe
2 min readBy:Today’s map highlights the extent to which European OECD countries rely on consumption tax revenue.
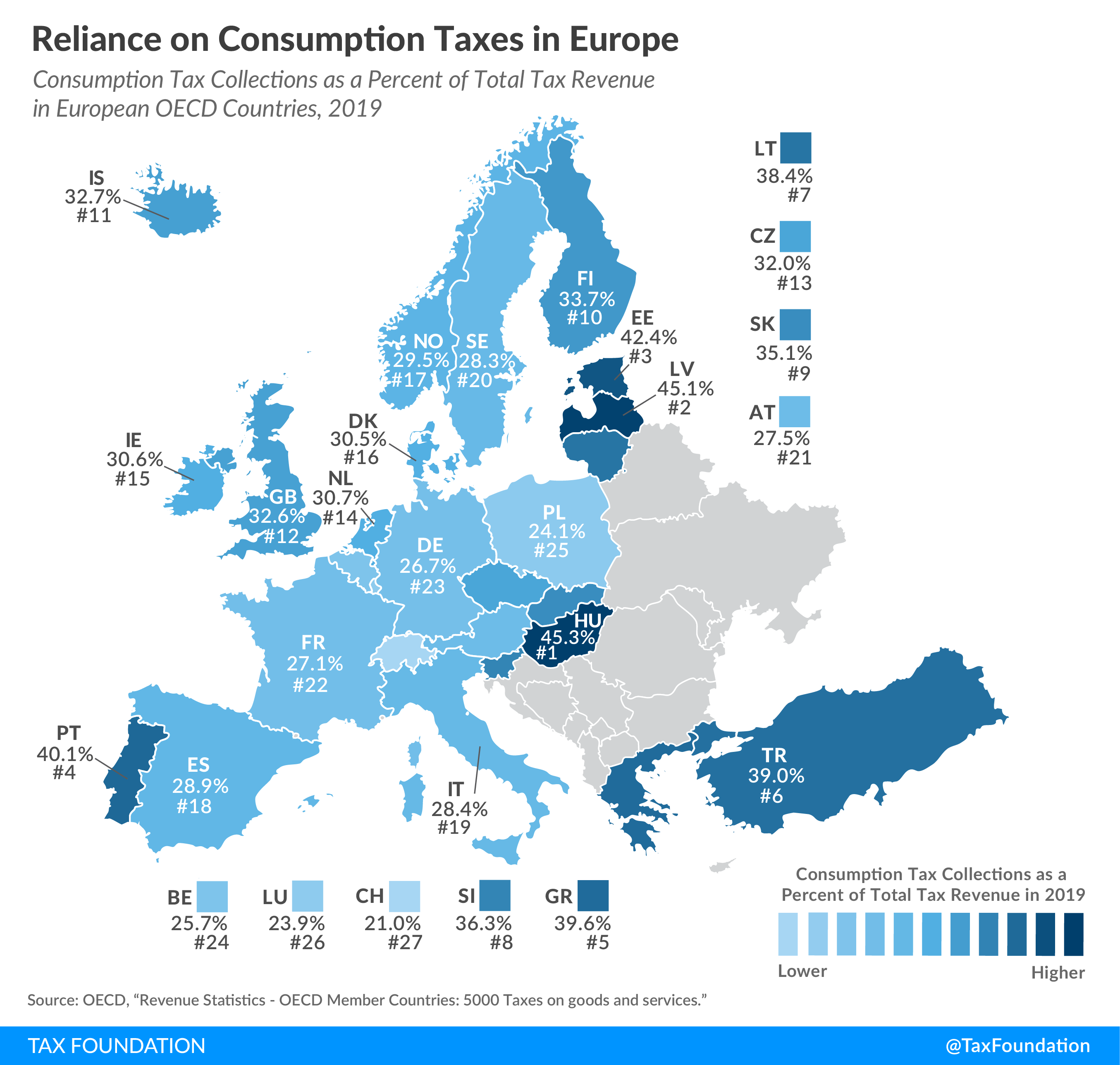
Consumption taxes are on goods and services. All European countries levy consumption taxes in the form of Value-added Taxes (VAT), excise taxes, and other taxes on goods and services. In 2019 (most recent data available), consumption taxes were the largest source of tax revenue in European OECD countries, at an average of 32.4 percent of total tax revenue.
In 2019, Hungary relied the most on consumption taxA consumption tax is typically levied on the purchase of goods or services and is paid directly or indirectly by the consumer in the form of retail sales taxes, excise taxes, tariffs, value-added taxes (VAT), or income taxes where all savings are tax-deductible. revenue, at 45.3 percent of total taxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities. revenue. Latvia had the second highest reliance on consumption taxes, at 45.1 percent, followed by Estonia at 42.4 percent.
Switzerland relied the least on consumption taxes in 2019, at 21.0 percent of total tax revenue. Luxembourg and Poland followed, at 23.9 percent and 24.1 percent, respectively.
As the following table shows, VAT revenue accounted on average for approximately two-thirds of all consumption tax revenue collected in 2019. Excise taxes and other taxes on goods and services accounted for the remaining third.
| Total Consumption Taxes (% of Total Tax Revenue) | VAT (% of Total Tax Revenue) | Excise Taxes and Other Taxes on Goods and Services (% of Total Tax Revenue) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Austria (AT) | 27.5% | 18.0% | 9.5% |
| Belgium (BE) | 25.7% | 15.6% | 10.1% |
| Czech Republic (CZ) | 32.0% | 21.7% | 10.3% |
| Denmark (DK) | 30.5% | 20.3% | 10.2% |
| Estonia (EE) | 42.4% | 26.7% | 15.7% |
| Finland (FI) | 33.7% | 21.7% | 12.0% |
| France (FR) | 27.1% | 15.9% | 11.2% |
| Germany (DE) | 26.7% | 18.3% | 8.4% |
| Greece (GR) | 39.6% | 21.3% | 18.3% |
| Hungary (HU) | 45.3% | 27.1% | 18.3% |
| Iceland (IS) | 32.7% | 23.6% | 9.2% |
| Ireland (IE) | 30.6% | 19.4% | 11.2% |
| Italy (IT) | 28.4% | 14.7% | 13.7% |
| Latvia (LV) | 45.1% | 27.7% | 17.4% |
| Lithuania (LT) | 38.4% | 26.2% | 12.2% |
| Luxembourg (LU) | 23.9% | 15.5% | 8.3% |
| Netherlands (NL) | 30.7% | 18.2% | 12.4% |
| Norway (NO) | 29.5% | 21.7% | 7.9% |
| Poland (PL) | 24.1% | 22.6% | 1.4% |
| Portugal (PT) | 40.1% | 25.4% | 14.6% |
| Slovak Republic (SK) | 35.1% | 20.9% | 14.3% |
| Slovenia (SI) | 36.3% | 21.5% | 14.8% |
| Spain (ES) | 28.9% | 18.8% | 10.1% |
| Sweden (SE) | 28.3% | 21.3% | 6.9% |
| Switzerland (CH) | 21.0% | 11.8% | 9.2% |
| Turkey (TR) | 39.0% | 18.1% | 20.9% |
| United Kingdom (GB) | 32.6% | 21.2% | 11.4% |
| Average | 32.4% | 20.6% | 11.8% |
|
Note: Individual items may not sum to total due to rounding. *For Greece, only the aggregate Taxes on Goods and Services was available for the year 2019. The share of VAT and Excise Taxes and Other Taxes on Goods and Services was calculated using 2018 data. Source: OECD, “Revenue Statistics – OECD Member Countries: Comparative Tables: 5000 Taxes on goods and services,” https://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=REV. |
|||
In 2019, reliance on VAT was highest in Latvia (27.7 percent), Hungary (27.1 percent), and Estonia (26.7 percent).
Switzerland relied the least on VAT revenue, at 11.8 percent of total tax revenue. This is partially because Switzerland has the lowest VAT rate of all countries covered, at only 7.7 percent. Italy (14.7 percent) and Luxembourg (15.5 percent) followed.
Note: This is part of a map series in which we examine tax revenue sources in Europe.
Stay informed on the tax policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted experts delivered straight to your inbox.
Subscribe