Executive Summary
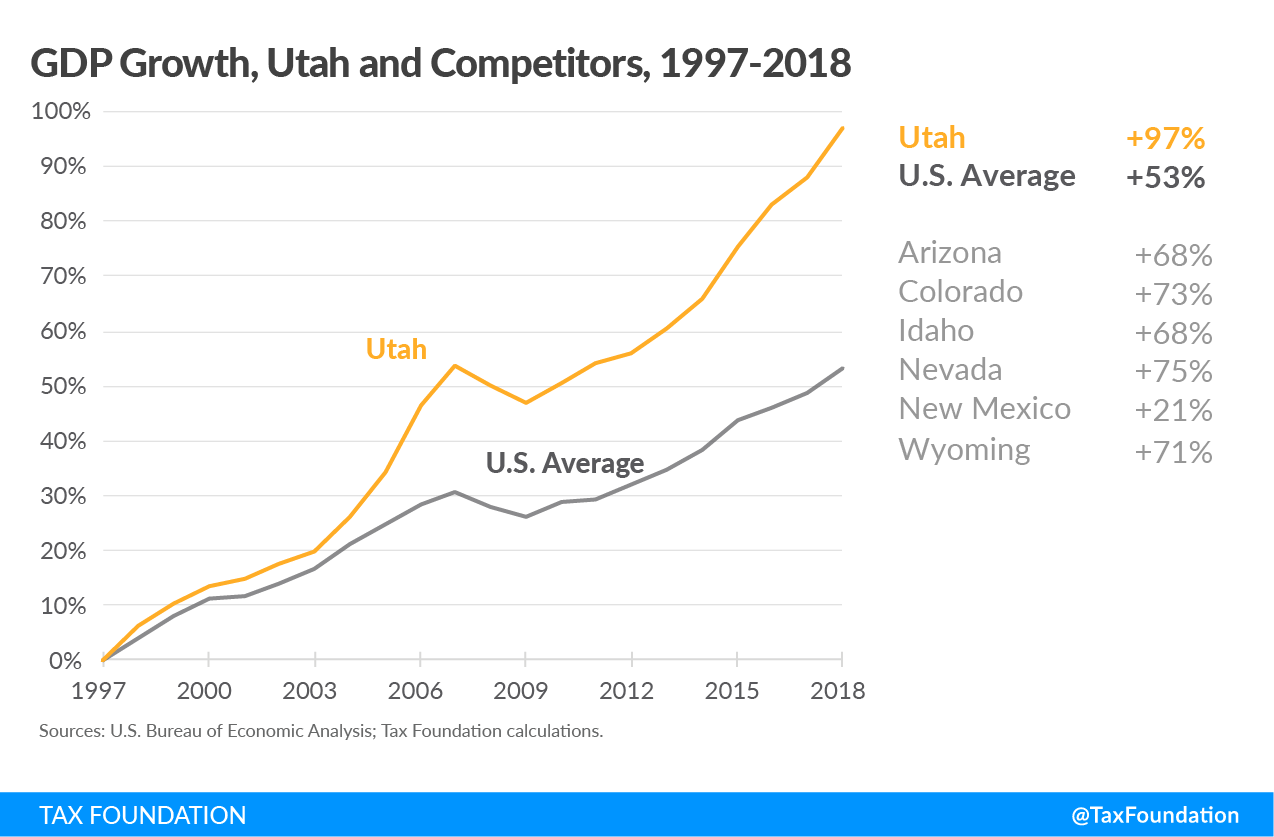
By almost any measure, Utah is, and deserves to be, the envy of its peers. The state’s economy has nearly doubled in size over the past two decades, growing at twice the rate of the nation at large. Income is rising, taxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities. collections are robust, and Utah leads the country in job growth. Tax reforms adopted in 2007 improved the structure and competitiveness of the state’s individual and corporate income taxes and established a model for other states to follow.
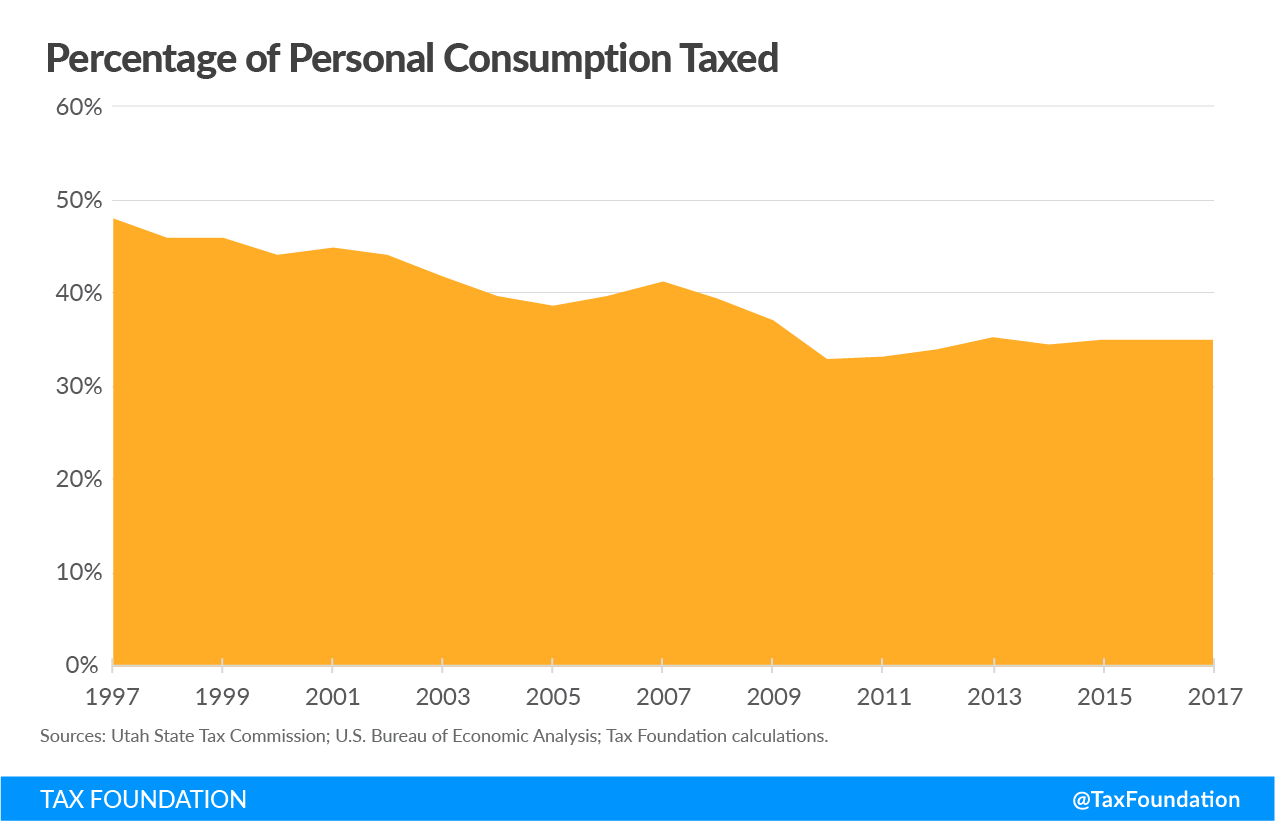
But today, some of the gains made in 2007 are being undone—not by conscious policy choices, but by their absence. The three-legged stool—income, property, and sales taxes—is increasingly unbalanced, to the detriment of the state’s economic competitiveness and revenue stability. Utah’s sales tax breadth is barely half what it was at its peak, shortly after the end of World War II, and the percentage of personal consumption subject to the tax has declined from nearly 50 percent to just 35 percent over the past 20 years.
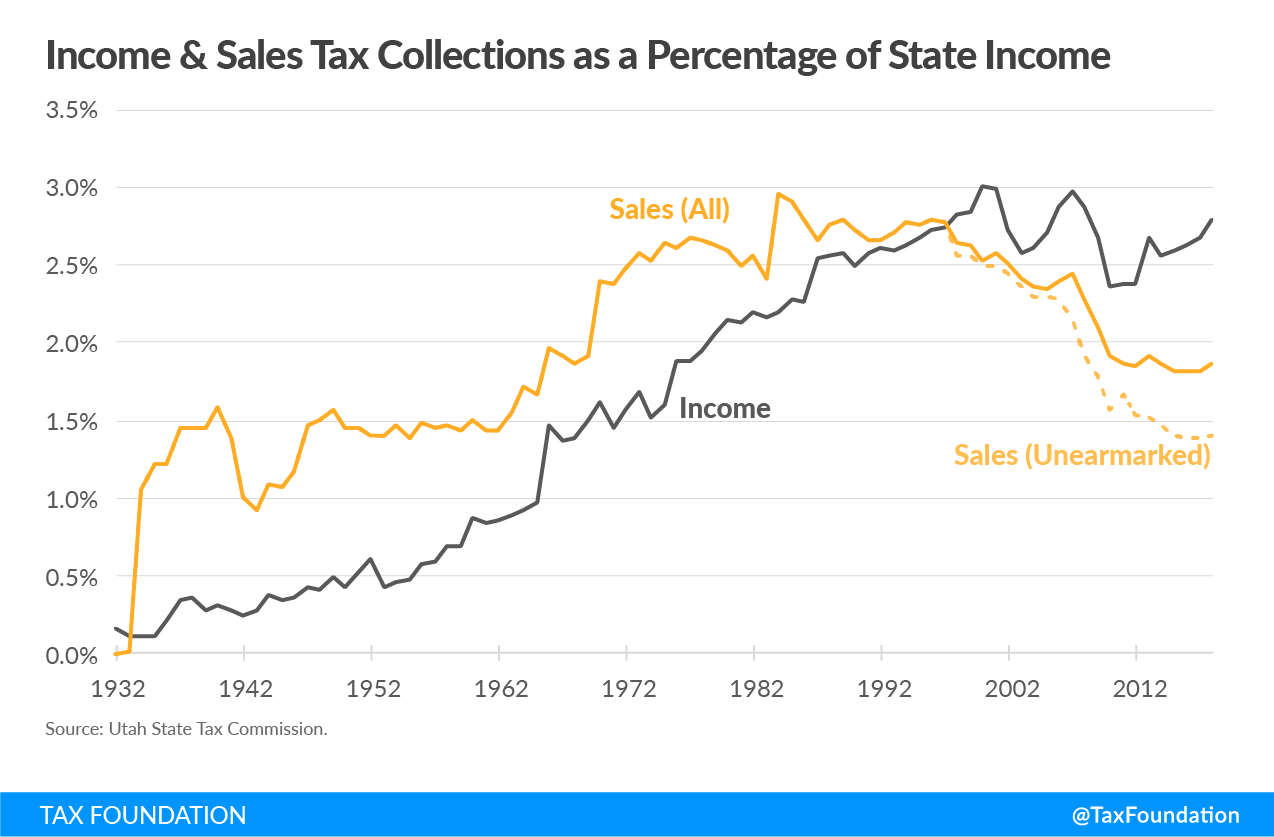
The result is a tax code that leans more heavily on income taxes, contrary to the intentions of tax reformers a little more than a decade ago, and a sales taxA sales tax is levied on retail sales of goods and services and, ideally, should apply to all final consumption with few exemptions. Many governments exempt goods like groceries; base broadening, such as including groceries, could keep rates lower. A sales tax should exempt business-to-business transactions which, when taxed, cause tax pyramiding. that increasingly puts a thumb on the scale, favoring some transactions over others. Alone among states, Utah earmarks the entirety of its individual and corporate income taxes and generates almost all its general fund revenue from the sales tax. Yet, over the past four decades, the sales tax has declined 31 percent as a share of state tax collections while the income tax is up 60 percent.
Utah does not have a revenue problem, but it does face a problem of imbalance. Shifting consumption patterns are eroding the sales tax, with untaxed services assuming an ever-greater share of personal consumption. The consequence is that the existing sales tax base is taxed at a higher rate than would otherwise be necessary, certain kinds of consumption are given preferential treatment, and the income tax—which is considerably less pro-growth than the sales tax and does not contribute to the general fund—has emerged as the dominant state tax.
The state’s sales tax is a reflection of its Depression-era roots and is constructed around an economy which long since vanished. Today’s economy has little in common with that of 1933, with higher incomes and changing consumer tastes shifting a greater share of consumption to services, while a digital economy upends traditional spending categories. A modernization is long overdue—for fairness, revenue stability, and a rebalancing of the tax code to secure the future of one of the more economically efficient forms of taxation available to states.
Sales tax reform follows the familiar refrain of “broad bases and lower rates,” but rather than simply speaking of broadening the base, we might instead speak of right-sizing the base. There is little question that the current sales tax baseThe tax base is the total amount of income, property, assets, consumption, transactions, or other economic activity subject to taxation by a tax authority. A narrow tax base is non-neutral and inefficient. A broad tax base reduces tax administration costs and allows more revenue to be raised at lower rates. is too narrow, arbitrarily exempting large swaths of personal consumption. But not all base-broadening measures are created equal.
There is a scholarly consensus that an ideal sales tax is imposed on all final consumption, both goods and services, but exempts all intermediate transactions (business inputs) to avoid tax pyramiding, where the same tax is embedded multiple times in the final purchase price. In contrast with this ideal, Utah’s base exempts the majority of personal consumption while over a quarter (and possibly considerably more) of current revenues are generated from business inputs. Although theoretical ideals may be out of reach, Utah policymakers should build on the state’s successes in reducing tax pyramidingTax pyramiding occurs when the same final good or service is taxed multiple times along the production process. This yields vastly different effective tax rates depending on the length of the supply chain and disproportionately harms low-margin firms. Gross receipts taxes are a prime example of tax pyramiding in action. by excluding intermediate purchases from base-broadening provisions, either excluding them by classifications of purchases or based on the identity of the purchaser.
Utah policymakers have wrestled with the proper definition of business inputs, with some advocating narrow definitions involving consumption of products that are “integral” to production or consumed in the production process, while others have advanced more expansive definitions which would exempt most business purchases. In these pages, we outline the negative ramifications of an overly narrow definition and how a poorly structured sales tax can increase consumer prices, disincentivize investment, and in many respects transform the sales tax into something else entirely.
This paper seeks to make the case for sales tax modernization. It also delves into questions of policy design, from the aforementioned exclusion of business inputs to rate-setting mechanisms to sourcing rules to ways to include local governments within the framework of reform. We also explore the possible use of sales tax base-broadening revenues to reduce individual income as well as sales tax rates. It is our hope that this analysis can help inform deliberations about the structure and implementation of a tax reform agenda.
We argue that legislators should avoid the temptation to chase a rate. Legislators should determine the appropriate sales tax base with reference to sound policy principles and adjust the rate accordingly rather than identifying a target rate and then pursuing whatever base-broadening measures are necessary to meet that target. The appropriate goal of revenue-neutral sales tax reform is a stable, economically neutral tax that reflects a 21st century economy, not the lowest possible rate.
We examine several options for phasing in sales tax base changes and for the inclusion of local governments. While policymakers can approach the local sales tax issue in several ways, it is important that local option sales taxes be included in any reforms—both base and rate changes. Doing otherwise introduces new complexities, puts state and local governments on divergent revenue trajectories, and renders Utah out of compliance with a multistate sales tax agreement that has taken on greater importance now that states have the legal authority to tax online sales.
We both discuss and apply several broadly accepted standards and observations about sales taxes, including that:
- Sales taxes should be imposed on goods and services alike, while exempting business inputs to avoid double taxationDouble taxation is when taxes are paid twice on the same dollar of income, regardless of whether that’s corporate or individual income. through tax pyramiding;
- The sales tax is more economically efficient than many competing forms of taxation, including the income tax, because it only falls on present consumption, not saving or investment;
- Because lower-income individuals have lower savings rates and consume a greater share of their income, the sales tax can be regressive, though broadening the base to include additional consumer services represents a progressive change;
- The sales tax scales well with ability to pay; and
- Consumption is a more stable tax base than income, though the failure to tax most consumer services is leading to a gradual erosion of sales tax revenues.
Conditions are ripe for reform. With the formation of a task force to consider sales tax modernization and other tax reform options, this is Utah’s chance to bequeath future generations a flexible tax code that can adapt to a changing economy, and a pro-growth tax code that harnesses Utahns’ work ethic and creative energy to continue—and build upon—the state’s many economic successes.
Share this article