Reliance on Individual Income Tax Revenue in Europe
1 min readBy:Today’s map shows the extent to which European countries rely on individual income tax revenue, measured as a share of total tax revenue.
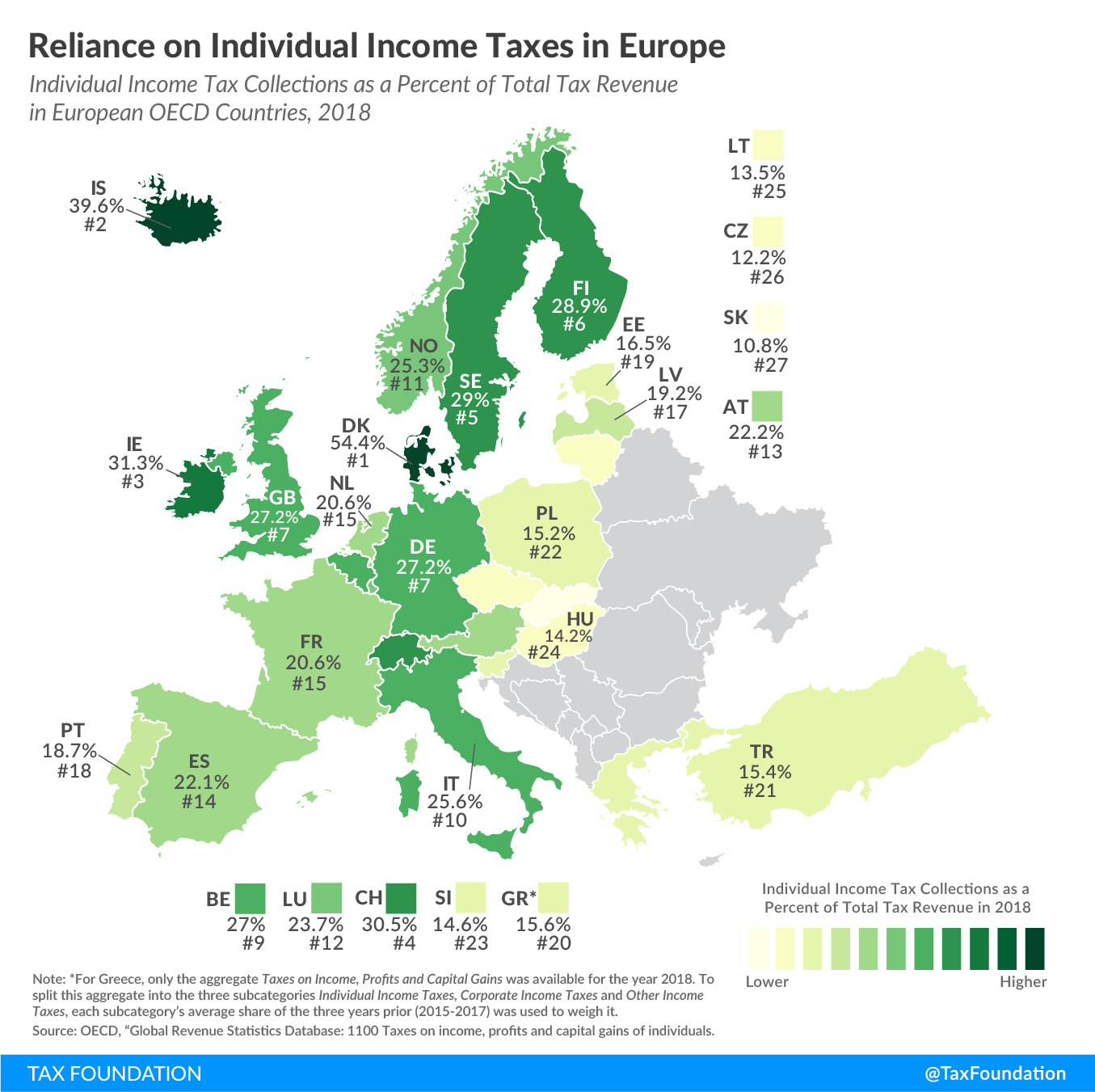
According to a recent report on taxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities. revenue sources, individual income taxes were the third most important tax revenue source among European OECD countries in 2018, at an average of 23.0 percent of total tax revenue. Only consumption taxes (32.5 percent) and social insurance taxes (29.7 percent) were on average greater sources of tax revenue.
Denmark relied the most on revenue from individual income taxes, at 54.4 percent of total tax revenue. This is partially because Denmark uses a share of its individual income taxAn individual income tax (or personal income tax) is levied on the wages, salaries, investments, or other forms of income an individual or household earns. The U.S. imposes a progressive income tax where rates increase with income. The Federal Income Tax was established in 1913 with the ratification of the 16th Amendment. Though barely 100 years old, individual income taxes are the largest source of tax revenue in the U.S. revenue for its social programs instead of levying a social insurance tax dedicated to fund these programs. Iceland and Ireland had the second and third highest reliance on individual income taxes, at 39.6 percent and 31.3 percent, respectively.
Slovakia (10.8 percent), the Czech Republic (12.2 percent), and Lithuania (13.5 percent) relied the least on individual income tax revenue. All three of these countries instead raised about two-thirds of their total tax revenue from social insurance taxes and consumption taxes combined.
Note: This is part of a map series in which we examine tax revenue sources in Europe.