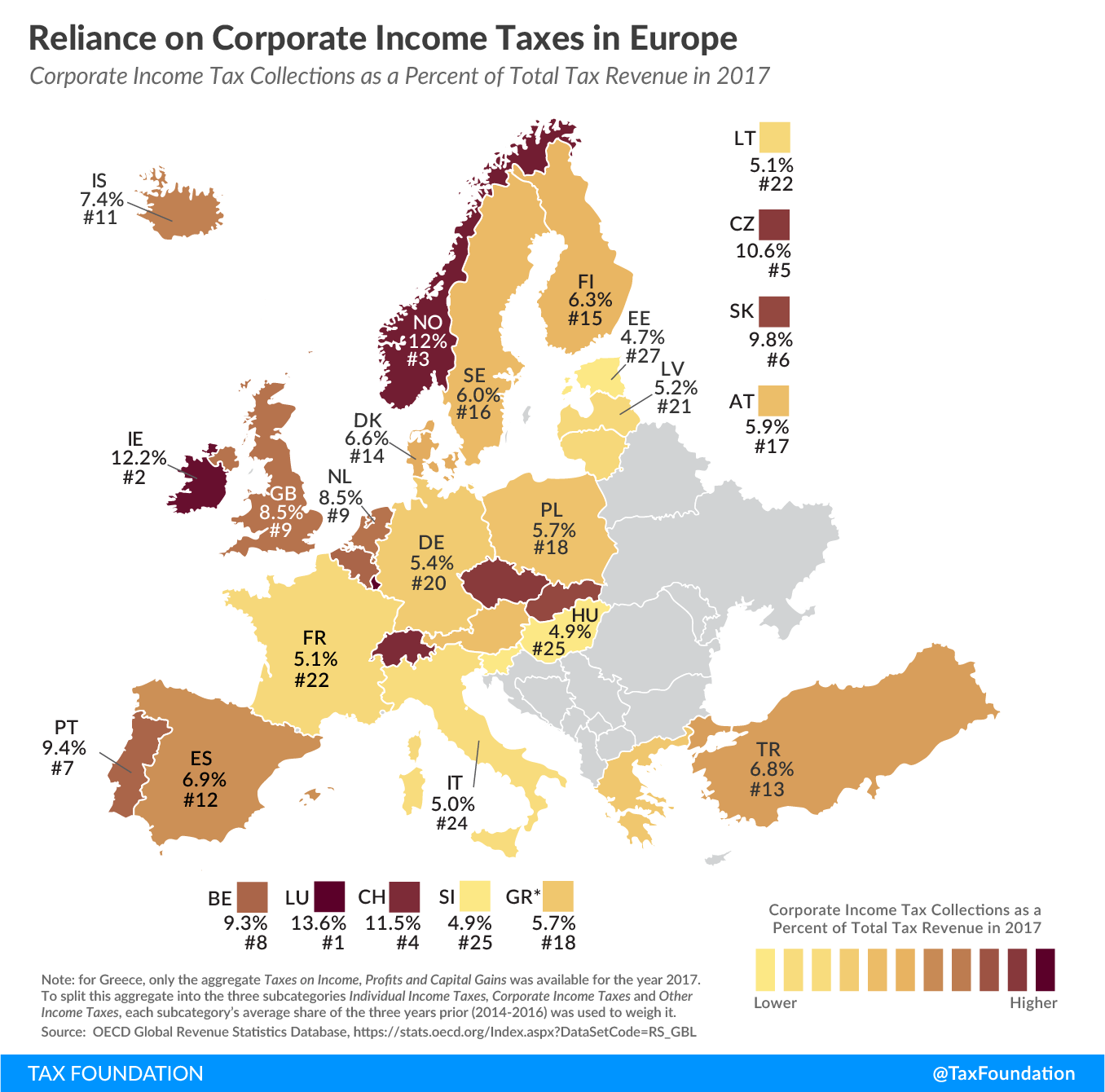
Reliance on Corporate Income Tax Revenue in Europe
1 min readBy:A recent report on taxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities. revenue sources shows the extent to which OECD countries rely on different tax types. Today’s map looks at the corporate income taxA corporate income tax (CIT) is levied by federal and state governments on business profits. Many companies are not subject to the CIT because they are taxed as pass-through businesses, with income reportable under the individual income tax. , which, compared to individual taxes, social insurance taxes, and consumption taxes, generates a relatively small share of tax revenue in Europe. In 2017, the most recent year for which data is available, the European countries covered in today’s map raised on average 7.5 percent of total tax revenue from corporate income taxes.
Luxembourg relied the most on its corporate income tax in 2017, at 13.6 percent of total tax revenue, followed by Ireland (12.2 percent) and Norway (12 percent). Estonia (4.7 percent), Slovenia (4.9 percent), and Hungary (4.9 percent) relied the least on the corporate income tax.
Despite declining corporate income tax rates over the last thirty years in Europe (and other parts of the world), average revenue from corporate income taxes as a share of total tax revenue has not declined since 1990. Many countries have been weakening their treatment of capital investment, which has led to broader tax bases and helped to offset the loss in corporate income tax revenue resulting from lower tax rates.
Corporate income taxes are a direct tax on corporate profits, and fluctuating business cycles can significantly impact these profits generated by businesses. This can make the corporate income tax a relatively volatile source of revenue.
Note: This is part of a map series in which we examine tax revenue sources in Europe.
Stay informed on the tax policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted experts delivered straight to your inbox.
Subscribe