A Partial Defense of the QBAI Exclusion
Lawmakers should consider maintaining QBAI and applying the several billion dollars from the Senate’s change toward other pro-growth international tax reforms instead.
6 min readKyle Pomerleau is a resident fellow at the American Enterprise Institute (AEI), where he studies federal tax policy.
Before joining AEI, Mr. Pomerleau was chief economist and vice president of economic analysis at the Tax Foundation, where he led the macroeconomic and tax modeling team and wrote on various tax policy topics, including corporate taxation, international tax policy, carbon taxation, and tax reform.
The author of many studies, Mr. Pomerleau has been published in trade publications and policy journals including Tax Notes and the National Tax Journal. He is frequently quoted in major media outlets such as The New York Times, The Wall Street Journal, and The Washington Post. He has also testified before Congress and state legislators.
Mr. Pomerleau has an MPP in economic and social policy from Georgetown University’s McCourt School of Public Policy and a BA in history and political science from the University of Southern Maine.

Lawmakers should consider maintaining QBAI and applying the several billion dollars from the Senate’s change toward other pro-growth international tax reforms instead.
6 min read
The Polish government is considering converting its traditional corporate income tax into a tax on distributed profits. We estimate that this reform would result in greater investment, a larger productive capital stock, and higher economic output in the long run.
29 min read
The UK’s adoption of full expensing is a welcome step that may generate short-run economic benefits. However, for the reform to have a meaningful effect on the UK’s international competitiveness and long-run economic performance, it must be made permanent—which the British government has said it hopes to do.
6 min read
For many years, the UK has adopted a strikingly ungenerous approach to capital cost recovery – the ability of firms to write off investment against tax. This has coincided with consistently low levels of business investment. The super-deduction, which has temporarily made the UK tax system much more supportive of capital investment in plant and machinery is set to expire.
34 min read
From a policy perspective it is appropriate to combat base erosion and profit shifting, but policymakers need to keep in mind the need for simplicity to avoid increasing the compliance burden on taxpayers and administrative burdens on tax authorities.
68 min read
The 2021 UK budget introduces a two-year super-deduction of 130 percent for plant and equipment and a delayed corporate tax rate increase from 19 percent to 25 percent in 2023. These policies have differential impacts on marginal effective tax rates for different assets, implying investment incentives will not be uniform.
15 min read

In our new report, we explore the design implications of a carbon tax and provide estimates for revenue, economic, and distributional effects of three potential carbon tax and revenue recycling proposals. Each proposal faces different trade-offs and achieves different policy goals.
23 min read
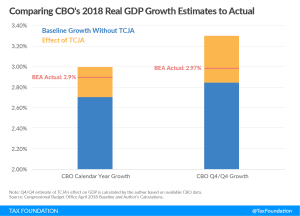

The U.S. decision to adopt a territorial tax system is certainly an improvement over having a worldwide system. However, in moving to a territorial system some of the new features created with the TCJA increased the complexity of the system.
38 min read
Warren’s comparison between the property tax and her proposed wealth tax makes a good sales pitch. However, there are important differences between the taxes. By no means is the property tax in many jurisdictions perfect, but it is generally better structured than a wealth tax.
4 min read

Sen. Elizabeth Warren introduced a 7 percent surtax on corporate profits called the “Real Corporate Profits Tax.” We estimate that this tax would reduce the incentive to invest in the United States, and result in a 1.9 percent smaller economy, a 3.3 percent smaller capital stock, and 1.5 percent lower wages. The surtax would raise $872 billion between 2020 and 2029 on a conventional basis and $476 billion on a dynamic basis. The tax would make the tax code more progressive, but it would fall on taxpayers in every income group.
9 min read
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act made significant changes to the way U.S. multinationals’ foreign profits are taxed. GILTI, or “Global Intangible Low Tax Income,” was introduced as an outbound anti-base erosion provision.
5 min read
Lawmakers recently introduced a bill to repeal the $10,000 cap on the state and local deduction (SALT) and raise the top tax rate on ordinary income from 37 percent to 39.6 percent.
4 min read
We estimate that a new proposal to expand the EITC would reduce federal revenue by $1.8 trillion and decrease long-run GDP by 0.29 percent, while boosting labor force participation for low-income tax filers by 822,788 full-time equivalent jobs.
10 min read
Sen. Elizabeth Warren recently proposed a wealth tax on high-net-worth individuals, a type of tax that is poorly targeted, difficult to administer, and raises constitutional questions.
4 min read
Due to a narrow tax base and a decrease in capital gains realizations, Congresswoman Ocasio-Cortez’s plan to tax income above $10 million would not raise as much revenue as intended. See our 10-year revenue estimates.
9 min read